 |
CopperSpice API
2.1.0
|
Provides the base functionality common to all socket types. More...
Public Typedefs | |
| using | BindMode = QFlags< BindFlag > |
| using | PauseModes = QFlags< PauseMode > |
 Public Typedefs inherited from QIODevice Public Typedefs inherited from QIODevice | |
| using | OpenMode = QFlags< OpenModeFlag > |
Public Types | |
| enum | BindFlag |
| enum | NetworkLayerProtocol |
| enum | PauseMode |
| enum | SocketError |
| enum | SocketOption |
| enum | SocketState |
| enum | SocketType |
 Public Types inherited from QIODevice Public Types inherited from QIODevice | |
| enum | OpenModeFlag |
Public Signals | |
| void | connected () |
| void | disconnected () |
| void | error (QAbstractSocket::SocketError socketError) |
| void | hostFound () |
| void | proxyAuthenticationRequired (const QNetworkProxy &proxy, QAuthenticator *authenticator) |
| void | stateChanged (QAbstractSocket::SocketState socketState) |
 Public Signals inherited from QIODevice Public Signals inherited from QIODevice | |
| void | aboutToClose () |
| void | bytesWritten (qint64 bytes) |
| void | readChannelFinished () |
| void | readyRead () |
 Public Signals inherited from QObject Public Signals inherited from QObject | |
| void | destroyed (QObject *obj=nullptr) |
| void | objectNameChanged (const QString &objectName) |
Public Methods | |
| QAbstractSocket (SocketType socketType, QObject *parent) | |
| virtual | ~QAbstractSocket () |
| void | abort () |
| bool | atEnd () const override |
| bool | bind (const QHostAddress &address, quint16 port=0, BindMode mode=DefaultForPlatform) |
| bool | bind (quint16 port=0, BindMode mode=DefaultForPlatform) |
| qint64 | bytesAvailable () const override |
| qint64 | bytesToWrite () const override |
| bool | canReadLine () const override |
| void | close () override |
| virtual void | connectToHost (const QHostAddress &address, quint16 port, OpenMode openMode=ReadWrite) |
| virtual void | connectToHost (const QString &hostName, quint16 port, OpenMode openMode=ReadWrite, NetworkLayerProtocol protocol=AnyIPProtocol) |
| virtual void | disconnectFromHost () |
| SocketError | error () const |
| bool | flush () |
| bool | isSequential () const override |
| bool | isValid () const |
| QHostAddress | localAddress () const |
| quint16 | localPort () const |
| PauseModes | pauseMode () const |
| QHostAddress | peerAddress () const |
| QString | peerName () const |
| quint16 | peerPort () const |
| QNetworkProxy | proxy () const |
| qint64 | readBufferSize () const |
| virtual void | resume () |
| void | setPauseMode (PauseModes pauseMode) |
| void | setProxy (const QNetworkProxy &networkProxy) |
| virtual void | setReadBufferSize (qint64 size) |
| virtual bool | setSocketDescriptor (qintptr socketDescriptor, SocketState socketState=ConnectedState, OpenMode openMode=ReadWrite) |
| virtual void | setSocketOption (QAbstractSocket::SocketOption option, const QVariant &value) |
| virtual qintptr | socketDescriptor () const |
| virtual QVariant | socketOption (QAbstractSocket::SocketOption option) |
| SocketType | socketType () const |
| SocketState | state () const |
| bool | waitForBytesWritten (int msecs=30000) override |
| virtual bool | waitForConnected (int msecs=30000) |
| virtual bool | waitForDisconnected (int msecs=30000) |
| bool | waitForReadyRead (int msecs=30000) override |
 Public Methods inherited from QIODevice Public Methods inherited from QIODevice | |
| QIODevice () | |
| QIODevice (QObject *parent) | |
| virtual | ~QIODevice () |
| QString | errorString () const |
| bool | getChar (char *c) |
| bool | isOpen () const |
| bool | isReadable () const |
| bool | isTextModeEnabled () const |
| bool | isWritable () const |
| virtual bool | open (OpenMode mode) |
| OpenMode | openMode () const |
| qint64 | peek (char *data, qint64 maxSize) |
| QByteArray | peek (qint64 maxSize) |
| virtual qint64 | pos () const |
| bool | putChar (char c) |
| qint64 | read (char *data, qint64 maxSize) |
| QByteArray | read (qint64 maxSize) |
| QByteArray | readAll () |
| qint64 | readLine (char *data, qint64 maxSize) |
| QByteArray | readLine (qint64 maxSize=0) |
| virtual bool | reset () |
| virtual bool | seek (qint64 pos) |
| void | setTextModeEnabled (bool enabled) |
| virtual qint64 | size () const |
| void | ungetChar (char c) |
| qint64 | write (const char *data) |
| qint64 | write (const char *data, qint64 maxSize) |
| qint64 | write (const QByteArray &data) |
 Public Methods inherited from QObject Public Methods inherited from QObject | |
| QObject (QObject *parent=nullptr) | |
| ~QObject () | |
| bool | blockSignals (bool block) |
| const QList< QObject * > & | children () const |
| bool | connect (const QObject *sender, const QString &signalMethod, const QString &location, const QString &slotMethod, Qt::ConnectionType type=Qt::AutoConnection) |
| bool | connect (const QObject *sender, const QString &signalMethod, const QString &slotMethod, Qt::ConnectionType type=Qt::AutoConnection) |
| bool | disconnect (const QObject *receiver, const QString &slotMethod=QString ()) const |
| bool | disconnect (const QString &signalMethod, const QString &location, const QObject *receiver=nullptr, const QString &slotMethod=QString ()) const |
| bool | disconnect (const QString &signalMethod=QString (), const QObject *receiver=nullptr, const QString &slotMethod=QString ()) const |
| void | dumpObjectInfo () |
| void | dumpObjectTree () |
| QList< QString > | dynamicPropertyNames () const |
| virtual bool | event (QEvent *event) |
| virtual bool | eventFilter (QObject *watched, QEvent *event) |
| template<typename T > | |
| T | findChild (const QString &childName=QString ()) const |
| template<class T > | |
| QList< T > | findChildren (const QRegularExpression ®Exp, Qt::FindChildOptions options=Qt::FindChildrenRecursively) const |
| template<class T > | |
| QList< T > | findChildren (const QString &childName=QString (), Qt::FindChildOptions options=Qt::FindChildrenRecursively) const |
| bool | inherits (const QString &className) const |
| void | installEventFilter (QObject *filterObj) |
| bool | isWidgetType () const |
| bool | isWindowType () const |
| void | killTimer (int id) |
| const QMetaObject * | metaObject () const |
| void | moveToThread (QThread *targetThread) |
| QString | objectName () const |
| QObject * | parent () const |
| template<class T = QVariant> | |
| T | property (const QString &name) const |
| void | removeEventFilter (QObject *obj) |
| void | setObjectName (const QString &name) |
| void | setParent (QObject *parent) |
| bool | setProperty (const QString &name, const QVariant &value) |
| bool | signalsBlocked () const |
| int | startTimer (int interval, Qt::TimerType timerType=Qt::CoarseTimer) |
| QThread * | thread () const |
Protected Methods | |
| qint64 | readData (char *data, qint64 maxlen) override |
| qint64 | readLineData (char *data, qint64 maxlen) override |
| void | setLocalAddress (const QHostAddress &address) |
| void | setLocalPort (quint16 port) |
| void | setPeerAddress (const QHostAddress &address) |
| void | setPeerName (const QString &name) |
| void | setPeerPort (quint16 port) |
| void | setSocketError (SocketError socketError) |
| void | setSocketState (SocketState state) |
| qint64 | writeData (const char *data, qint64 len) override |
 Protected Methods inherited from QIODevice Protected Methods inherited from QIODevice | |
| void | setErrorString (const QString &errorString) |
| void | setOpenMode (OpenMode openMode) |
 Protected Methods inherited from QObject Protected Methods inherited from QObject | |
| virtual void | childEvent (QChildEvent *event) |
| virtual void | connectNotify (const QMetaMethod &signalMethod) const |
| virtual void | customEvent (QEvent *event) |
| virtual void | disconnectNotify (const QMetaMethod &signalMethod) const |
| bool | isSignalConnected (const QMetaMethod &signalMethod) const |
| int | receivers (const QString &signal) const |
| QObject * | sender () const |
| int | senderSignalIndex () const |
| virtual void | timerEvent (QTimerEvent *event) |
Additional Inherited Members | |
 Public Slots inherited from QObject Public Slots inherited from QObject | |
| void | deleteLater () |
 Static Public Methods inherited from QObject Static Public Methods inherited from QObject | |
| static bool | connect (const QObject *sender, const QMetaMethod &signalMethod, const QObject *receiver, const QMetaMethod &slotMethod, Qt::ConnectionType type=Qt::AutoConnection) |
| static bool | connect (const QObject *sender, const QString &signalMethod, const QObject *receiver, const QString &slotMethod, Qt::ConnectionType type=Qt::AutoConnection, const QString &location=QString ()) |
| static bool | connect (const QObject *sender, const QString &signalMethod, const QString &location, const QObject *receiver, const QString &slotMethod, Qt::ConnectionType type=Qt::AutoConnection) |
| template<class Sender , class SignalClass , class... SignalArgs, class Receiver , class SlotClass , class... SlotArgs, class SlotReturn > | |
| static bool | connect (const Sender *sender, void (SignalClass::*signalMethod)(SignalArgs...), const Receiver *receiver, SlotReturn (SlotClass::*slotMethod)(SlotArgs...), Qt::ConnectionType type=Qt::AutoConnection) |
| template<class Sender , class SignalClass , class... SignalArgs, class Receiver , class T > | |
| static bool | connect (const Sender *sender, void (SignalClass::*signalMethod)(SignalArgs...), const Receiver *receiver, T slotLambda, Qt::ConnectionType type=Qt::AutoConnection) |
| static bool | disconnect (const QObject *sender, const QMetaMethod &signalMethod, const QObject *receiver, const QMetaMethod &slotMethod) |
| static bool | disconnect (const QObject *sender, const QString &signalMethod, const QObject *receiver, const QString &slotMethod) |
| static bool | disconnect (const QObject *sender, const QString &signalMethod, const QString &location, const QObject *receiver, const QString &slotMethod) |
| static bool | disconnect (const QObject *sender, std::nullptr_t, const QObject *receiver, std::nullptr_t) |
| template<class Sender , class SignalClass , class... SignalArgs, class Receiver , class SlotClass , class... SlotArgs, class SlotReturn > | |
| static bool | disconnect (const Sender *sender, void (SignalClass::*signalMethod)(SignalArgs...), const Receiver *receiver, SlotReturn (SlotClass::*slotMethod)(SlotArgs...)) |
| template<class Sender , class SignalClass , class... SignalArgs, class Receiver > | |
| static bool | disconnect (const Sender *sender, void (SignalClass::*signalMethod)(SignalArgs...), const Receiver *receiver, std::nullptr_t slotMethod=nullptr) |
| template<class Sender , class SignalClass , class... SignalArgs, class Receiver , class T > | |
| static bool | disconnect (const Sender *sender, void (SignalClass::*signalMethod)(SignalArgs...), const Receiver *receiver, T slotMethod) |
| static QMetaObject & | staticMetaObject () |
| static QString | tr (const char *text, const char *comment=nullptr, std::optional< int > numArg=std::optional< int >()) |
 Properties inherited from QObject Properties inherited from QObject | |
| objectName | |
 Related Functions inherited from QObject Related Functions inherited from QObject | |
| T | qobject_cast (QObject *object) |
| QObjectList | |
Detailed Description
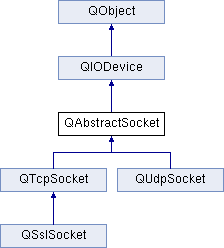
The QAbstractSocket class provides the base functionality common to all socket types. QAbstractSocket is the base class for QTcpSocket and QUdpSocket and contains all common functionality of these two classes. If you need a socket there are two options:
- Instantiate QTcpSocket or QUdpSocket.
- Create a native socket descriptor, instantiate QAbstractSocket, and call setSocketDescriptor() to wrap the native socket.
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) is a reliable, stream-oriented, connection-oriented transport protocol. UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is an unreliable, datagram-oriented, connectionless protocol. In practice, this means that TCP is better suited for continuous transmission of data, whereas the more lightweight UDP can be used when reliability is not important.
QAbstractSocket's API unifies most of the differences between the two protocols. For example, although UDP is connectionless, connectToHost() establishes a virtual connection for UDP sockets, enabling you to use QAbstractSocket in more or less the same way regardless of the underlying protocol. Internally, QAbstractSocket remembers the address and port passed to connectToHost(), and functions like read() and write() use these values.
At any time, QAbstractSocket has a state (returned by state()). The initial state is UnconnectedState. After calling connectToHost(), the socket first enters HostLookupState. If the host is found, QAbstractSocket enters ConnectingState and emits the hostFound() signal. When the connection has been established, it enters ConnectedState and emits connected(). If an error occurs at any stage, error() is emitted. Whenever the state changes, stateChanged() is emitted. For convenience, isValid() returns true if the socket is ready for reading and writing, but note that the socket's state must be ConnectedState before reading and writing can occur.
Read or write data by calling read() or write() or use the methods readLine() and readAll(). QAbstractSocket also inherits getChar(), putChar(), and ungetChar() from QIODevice, which work on single bytes. The bytesWritten() signal is emitted when data has been written to the socket (i.e., when the client has read the data). Note that CopperSpice does not limit the write buffer size. You can monitor its size by listening to this signal.
The readyRead() signal is emitted every time a new chunk of data has arrived. bytesAvailable() then returns the number of bytes that are available for reading. Typically, you would connect the readyRead() signal to a slot and read all available data there. If you do not read all the data at once, the remaining data will still be available later, and any new incoming data will be appended to QAbstractSocket's internal read buffer. To limit the size of the read buffer, call setReadBufferSize().
To close the socket, call disconnectFromHost(). QAbstractSocket enters QAbstractSocket::ClosingState. After all pending data has been written to the socket, QAbstractSocket actually closes the socket, enters QAbstractSocket::ClosedState, and emits disconnected(). If you want to abort a connection immediately, discarding all pending data, call abort() instead. If the remote host closes the connection, QAbstractSocket will emit error(QAbstractSocket::RemoteHostClosedError), during which the socket state will still be ConnectedState, and then the disconnected() signal will be emitted.
The port and address of the connected peer is fetched by calling peerPort() and peerAddress(). peerName() returns the host name of the peer, as passed to connectToHost(). localPort() and localAddress() return the port and address of the local socket.
QAbstractSocket provides a set of functions that suspend the calling thread until certain signals are emitted. These functions can be used to implement blocking sockets:
- waitForConnected() blocks until a connection has been established.
- waitForReadyRead() blocks until new data is available for reading.
- waitForBytesWritten() blocks until one payload of data has been written to the socket.
- waitForDisconnected() blocks until the connection has closed.
If waitForReadyRead() returns false, the connection has been closed or an error has occurred.
Programming with a blocking socket is radically different from programming with a non-blocking socket. A blocking socket does not require an event loop and typically leads to simpler code. However, in a GUI application, blocking sockets should only be used in non-GUI threads, to avoid freezing the user interface.
- Note
- We discourage the use of the blocking functions together with signals. One of the two possibilities should be used.
QAbstractSocket can be used with QTextStream and QDataStream's stream operators (operator<<() and operator>>()). There is one issue to be aware of, though: You must make sure that enough data is available before attempting to read it using operator>>().
- See also
- QFtp, QNetworkAccessManager, QTcpServer
Member Typedef Documentation
Typedef for QFlags<BindFlag> which contains an OR combination of BindFlag values.
Refer to QAbstractSocket::BindFlag for the enum documentation.
Typedef for QFlags<PauseMode> which contains an OR combination of PauseMode values.
Refer to QAbstractSocket::PauseMode for the enum documentation.
Member Enumeration Documentation
This enum describes the different flags you can pass to modify the behavior of QAbstractSocket::bind().
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
QAbstractSocket::ShareAddress | 0x1 | Allow other services to bind to the same address and port. This is useful when multiple processes share the load of a single service by listening to the same address and port (e.g., a web server with several pre-forked listeners can greatly improve response time). However, because any service is allowed to rebind, this option is subject to certain security considerations. Note that by combining this option with ReuseAddressHint, you will also allow your service to rebind an existing shared address. On Unix, this is equivalent to the SO_REUSEADDR socket option. On Windows, this option is ignored. |
QAbstractSocket::DontShareAddress | 0x2 | Bind the address and port exclusively, so that no other services are allowed to rebind. By passing this option to QAbstractSocket::bind(), you are guaranteed that on success, your service is the only one that listens to the address and port. No services are allowed to rebind, even if they pass ReuseAddressHint. This option provides more security than ShareAddress, but on certain operating systems, it requires you to run the server with administrator privileges. On Unix and OS X, not sharing is the default behavior for binding an address and port, so this option is ignored. On Windows, this option uses the SO_EXCLUSIVEADDRUSE socket option. |
QAbstractSocket::ReuseAddressHint | 0x4 | Provides a hint to QAbstractSocket that it should try to rebind the service even if the address and port are already bound by another socket. On Windows and Unix, this is equivalent to the SO_REUSEADDR socket option. |
QAbstractSocket::DefaultForPlatform | 0x0 | The default option for the current platform. On Unix and Mac OS X, this is equivalent to (DontShareAddress + ReuseAddressHint), and on Windows, its equivalent to ShareAddress. |
This enum describes the network layer protocol values.
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
QAbstractSocket::IPv4Protocol | 0 | IPv4 |
QAbstractSocket::IPv6Protocol | 1 | IPv6 |
QAbstractSocket::UnknownNetworkLayerProtocol | -1 | Other than IPv4 and IPv6 |
- See also
- QHostAddress::protocol()
This enum describes the behavior of when the socket should hold back with continuing data transfer. The only notification currently supported is QSslSocket::sslErrors().
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
QAbstractSocket::PauseNever | 0x0 | Do not pause data transfer on the socket. This is the default and matches the behavior from earlier versions of QAbstractSocket. |
QAbstractSocket::PauseOnSslErrors | 0x1 | Pause data transfer on the socket upon receiving an SSL error notification. For example, QSslSocket::sslErrors(). |
This enum describes the socket errors that can occur.
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
QAbstractSocket::ConnectionRefusedError | 0 | The connection was refused by the peer (or timed out). |
QAbstractSocket::RemoteHostClosedError | 1 | The remote host closed the connection. Note that the client socket (i.e., this socket) will be closed after the remote close notification has been sent. |
QAbstractSocket::HostNotFoundError | 2 | The host address was not found. |
QAbstractSocket::SocketAccessError | 3 | The socket operation failed because the application lacked the required privileges. |
QAbstractSocket::SocketResourceError | 4 | The local system ran out of resources (e.g., too many sockets). |
QAbstractSocket::SocketTimeoutError | 5 | The socket operation timed out. |
QAbstractSocket::DatagramTooLargeError | 6 | The datagram was larger than the operating system's limit (which can be as low as 8192 bytes). |
QAbstractSocket::NetworkError | 7 | An error occurred with the network (e.g., the network cable was accidentally plugged out). |
QAbstractSocket::AddressInUseError | 8 | The address specified to QUdpSocket::bind() is already in use and was set to be exclusive. |
QAbstractSocket::SocketAddressNotAvailableError | 9 | The address specified to QUdpSocket::bind() does not belong to the host. |
QAbstractSocket::UnsupportedSocketOperationError | 10 | The requested socket operation is not supported by the local operating system (e.g., lack of IPv6 support). |
QAbstractSocket::ProxyAuthenticationRequiredError | 12 | The socket is using a proxy, and the proxy requires authentication. |
QAbstractSocket::SslHandshakeFailedError | 13 | The SSL/TLS handshake failed, so the connection was closed (only used in QSslSocket) |
QAbstractSocket::UnfinishedSocketOperationError | 11 | Used by QAbstractSocketEngine only, The last operation attempted has not finished yet (still in progress in the background) |
QAbstractSocket::ProxyConnectionRefusedError | 14 | Could not contact the proxy server because the connection to that server was denied. |
QAbstractSocket::ProxyConnectionClosedError | 15 | The connection to the proxy server was closed unexpectedly (before the connection to the final peer was established) |
QAbstractSocket::ProxyConnectionTimeoutError | 16 | The connection to the proxy server timed out or the proxy server stopped responding in the authentication phase. |
QAbstractSocket::ProxyNotFoundError | 17 | The proxy address set with setProxy() (or the application proxy) was not found. |
QAbstractSocket::ProxyProtocolError | 18 | The connection negotiation with the proxy server because the response from the proxy server could not be understood. |
QAbstractSocket::UnknownSocketError | -1 | An unidentified error occurred. |
- See also
- QAbstractSocket::error()
This enum represents the options that can be set on a socket. If desired, they can be set after having received the connected() signal from the socket or after having received a new socket from a QTcpServer.
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
QAbstractSocket::LowDelayOption | 0 | Try to optimize the socket for low latency. For a QTcpSocket this would set the TCP_NODELAY option and disable Nagle's algorithm. Set this to 1 to enable. |
QAbstractSocket::KeepAliveOption | 1 | Set this to 1 to enable the SO_KEEPALIVE socket option |
QAbstractSocket::MulticastTtlOption | 2 | Set this to an integer value to set IP_MULTICAST_TTL (TTL for multicast datagrams) socket option. |
QAbstractSocket::MulticastLoopbackOption | 3 | Set this to 1 to enable the IP_MULTICAST_LOOP (multicast loopback) socket option. |
This enum describes the different states in which a socket can be.
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
QAbstractSocket::UnconnectedState | 0 | The socket is not connected. |
QAbstractSocket::HostLookupState | 1 | The socket is performing a host name lookup. |
QAbstractSocket::ConnectingState | 2 | The socket has started establishing a connection. |
QAbstractSocket::ConnectedState | 3 | A connection is established. |
QAbstractSocket::BoundState | 4 | The socket is bound to an address and port (for servers). |
QAbstractSocket::ClosingState | 6 | The socket is about to close (data may still be waiting to be written). |
QAbstractSocket::ListeningState | 5 | For internal use only. |
- See also
- QAbstractSocket::state()
This enum describes the transport layer protocol.
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
QAbstractSocket::TcpSocket | 0 | TCP |
QAbstractSocket::UdpSocket | 1 | UDP |
QAbstractSocket::UnknownSocketType | -1 | Other than TCP and UDP |
- See also
- QAbstractSocket::socketType()
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
| QAbstractSocket::QAbstractSocket | ( | SocketType | socketType, |
| QObject * | parent | ||
| ) |
Creates a new abstract socket of type socketType. The parent object is passed to the QObject constructor.
- See also
- socketType(), QTcpSocket, QUdpSocket
|
virtual |
Destroys the socket.
Method Documentation
| void QAbstractSocket::abort | ( | ) |
Aborts the current connection and resets the socket. Unlike disconnectFromHost(), this method immediately closes the socket, discarding any pending data in the write buffer.
- See also
- disconnectFromHost(), close()
|
overridevirtual |
Returns true if no more data is currently available for reading, otherwise returns false. This method is most commonly used when reading data from the socket in a loop.
- See also
- bytesAvailable(), readyRead()
Reimplemented from QIODevice::atEnd()
Reimplemented in QSslSocket::atEnd()
| bool QAbstractSocket::bind | ( | const QHostAddress & | address, |
| quint16 | port = 0, |
||
| BindMode | mode = DefaultForPlatform |
||
| ) |
Binds to address on port using the given mode. By default the socket is bound using the value DefaultForPlatform in the enum BindMode. If a port is not specified a random port is chosen. On success this method returns true and the socket enters the value BoundState in the enum SocketState, otherwise it returns false.
For UDP sockets, after binding, the signal QUdpSocket::readyRead() is emitted whenever a UDP datagram arrives on the specified address and port. For TCP sockets, this method may be used to specify which interface to use for an outgoing connection, which is useful in case of multiple network interfaces.
Binds to QHostAddress:Any on port using the given mode. By default the socket is bound using the DefaultForPlatform in the enum BindMode. If a port is not specified a random port is chosen.
|
overridevirtual |
Returns the number of incoming bytes that are waiting to be read.
- See also
- bytesToWrite(), read()
Reimplemented from QIODevice::bytesAvailable()
Reimplemented in QSslSocket::bytesAvailable()
|
overridevirtual |
Returns the number of bytes that are waiting to be written. The bytes are written when control goes back to the event loop or when flush() is called.
- See also
- bytesAvailable(), flush()
Reimplemented from QIODevice::bytesToWrite()
Reimplemented in QSslSocket::bytesToWrite()
|
overridevirtual |
Returns true if a line of data can be read from the socket, otherwise returns false.
- See also
- readLine()
Reimplemented from QIODevice::canReadLine()
Reimplemented in QSslSocket::canReadLine()
|
overridevirtual |
Closes the I/O device for the socket, disconnects the socket's connection with the host, closes the socket, and resets the name, address, port number and underlying socket descriptor.
Refer to QIODevice::close() for a description of the actions that occur when an I/O device is closed.
- See also
- abort()
Reimplemented from QIODevice::close()
Reimplemented in QSslSocket::close()
|
signal |
This signal is emitted after connectToHost() has been called and a connection has been successfully established.
On some operating systems the connected() signal may be directly emitted from the connectToHost() call for connections to the localhost.
- See also
- connectToHost(), disconnected()
|
virtual |
Attempts to make a connection to address on the given port.
|
virtual |
Attempts to make a connection to hostname on the given port.
The socket is opened in the given openMode and first enters HostLookupState, then performs a host name lookup of hostName. If the lookup succeeds, hostFound() is emitted and QAbstractSocket enters ConnectingState. It then attempts to connect to the address or addresses returned by the lookup. Finally, if a connection is established, QAbstractSocket enters ConnectedState and emits connected().
At any point the socket can emit error() to signal that an error occurred.
The parameter hostName can be an IP address like "127.0.0.1" or it can be a host name like "example.com". QAbstractSocket will do a lookup only if required. The port is in native byte order.
- See also
- state(), peerName(), peerAddress(), peerPort(), waitForConnected()
Reimplemented in QSslSocket::connectToHost()
|
signal |
This signal is emitted when the socket has been disconnected.
- Warning
- If you need to delete the sender() of this signal in a slot connected to it, use the deleteLater() method.
- See also
- connectToHost(), disconnectFromHost(), abort()
|
virtual |
Attempts to close the socket. If there is pending data waiting to be written, QAbstractSocket will enter ClosingState and wait until all data has been written. Eventually, it will enter UnconnectedState and emit the disconnected() signal.
- See also
- connectToHost()
Reimplemented in QSslSocket::disconnectFromHost()
| SocketError QAbstractSocket::error | ( | ) | const |
Returns the type of error that last occurred.
- See also
- state(), errorString()
|
signal |
This signal is emitted after an error occurred. The socketError parameter describes the type of error that occurred.
- See also
- error(), errorString(), Creating Custom Types
| bool QAbstractSocket::flush | ( | ) |
This method writes as much as possible from the internal write buffer to the underlying network socket, without blocking. If any data was written, this method returns true, otherwise false is returned.
Call this method if you need QAbstractSocket to start sending buffered data immediately. The number of bytes successfully written depends on the operating system. In most cases, you do not need to call this method, because QAbstractSocket will start sending data automatically once control goes back to the event loop. In the absence of an event loop, call waitForBytesWritten() instead.
- See also
- write(), waitForBytesWritten()
|
signal |
This signal is emitted after connectToHost() has been called and the host lookup has succeeded.
- Note
- QAbstractSocket may emit hostFound() directly from the connectToHost() call since a DNS result could have been cached.
- See also
- connected()
|
overridevirtual |
Reimplemented from QIODevice::isSequential()
| bool QAbstractSocket::isValid | ( | ) | const |
Returns true if the socket is valid and ready for use, otherwise returns false.
- Note
- The socket's state must be ConnectedState before reading and writing can occur.
- See also
- state()
| QHostAddress QAbstractSocket::localAddress | ( | ) | const |
Returns the host address of the local socket if available, otherwise returns QHostAddress::Null.
This is normally the main IP address of the host, but can be QHostAddress::LocalHost (127.0.0.1) for connections to the local host.
- See also
- localPort(), peerAddress(), setLocalAddress()
| quint16 QAbstractSocket::localPort | ( | ) | const |
Returns the host port number (in native byte order) of the local socket if available, otherwise returns 0.
- See also
- localAddress(), peerPort(), setLocalPort()
| QAbstractSocket::PauseModes QAbstractSocket::pauseMode | ( | ) | const |
Returns the pause mode of this socket.
- See also
- setPauseMode(), resume()
| QHostAddress QAbstractSocket::peerAddress | ( | ) | const |
Returns the address of the connected peer if the socket is in ConnectedState, otherwise returns QHostAddress::Null.
- See also
- peerName(), peerPort(), localAddress(), setPeerAddress()
| QString QAbstractSocket::peerName | ( | ) | const |
Returns the name of the peer as specified by connectToHost(), or an empty QString if connectToHost() has not been called.
- See also
- peerAddress(), peerPort(), setPeerName()
| quint16 QAbstractSocket::peerPort | ( | ) | const |
Returns the port of the connected peer if the socket is in ConnectedState, otherwise returns 0.
- See also
- peerAddress(), localPort(), setPeerPort()
| QNetworkProxy QAbstractSocket::proxy | ( | ) | const |
Returns the network proxy for this socket. By default QNetworkProxy::DefaultProxy is used, which means this socket will query the default proxy settings for the application.
- See also
- setProxy(), QNetworkProxy, QNetworkProxyFactory
|
signal |
This signal can be emitted when a proxy that requires authentication is used. The authenticator object can then be filled in with the required details to allow authentication and continue the connection.
- Note
- It is not possible to use a QueuedConnection to connect to this signal, as the connection will fail if the authenticator has not been filled in with new information when the signal returns.
- See also
- QAuthenticator, QNetworkProxy
| qint64 QAbstractSocket::readBufferSize | ( | ) | const |
Returns the size of the internal read buffer. This limits the amount of data that the client can receive before you call read() or readAll().
A read buffer size of 0 (the default) means that the buffer has no size limit, ensuring that no data is lost.
- See also
- setReadBufferSize(), read()
Implements QIODevice::readData()
Reimplemented in QSslSocket::readData()
Reimplemented from QIODevice::readLineData()
|
virtual |
Continues data transfer on the socket. This method should only be used after the socket has been set to pause upon notifications and a notification has been received. The only notification currently supported is QSslSocket::sslErrors(). Calling this method if the socket is not paused results in undefined behavior.
- See also
- pauseMode(), setPauseMode()
Reimplemented in QSslSocket::resume()
|
protected |
Sets the address on the local side of a connection to address.
You can call this method in a subclass of QAbstractSocket to change the return value of the localAddress() method after a connection has been established. This feature is commonly used by proxy connections for virtual connection settings.
This method does not bind the local address of the socket prior to a connection (e.g., QUdpSocket::bind()).
- See also
- localAddress(), setLocalPort(), setPeerAddress()
|
protected |
Sets the port on the local side of a connection to port.
You can call this method in a subclass of QAbstractSocket to change the return value of the localPort() method after a connection has been established. This feature is commonly used by proxy connections for virtual connection settings.
Note that this method does not bind the local port of the socket prior to a connection (e.g., QUdpSocket::bind()).
- See also
- localPort(), localAddress(), setLocalAddress(), setPeerPort()
| void QAbstractSocket::setPauseMode | ( | PauseModes | pauseMode | ) |
Controls whether to pause upon receiving a notification. The pauseMode parameter specifies the conditions in which the socket should be paused. The only notification currently supported is QSslSocket::sslErrors(). If set to PauseOnSslErrors, data transfer on the socket will be paused and needs to be enabled explicitly again by calling resume(). By default this option is set to PauseNever. This option must be called before connecting to the server, otherwise it will result in undefined behavior.
- See also
- pauseMode(), resume()
|
protected |
Sets the address of the remote side of the connection to address.
You can call this method in a subclass of QAbstractSocket to change the return value of the peerAddress() method after a connection has been established. This feature is commonly used by proxy connections for virtual connection settings.
- See also
- peerAddress(), setPeerPort(), setLocalAddress()
|
protected |
Sets the host name of the remote peer to name.
You can call this method in a subclass of QAbstractSocket to change the return value of the peerName() method after a connection has been established. This feature is commonly used by proxy connections for virtual connection settings.
- See also
- peerName()
|
protected |
Sets the port of the remote side of the connection to port.
You can call this method in a subclass of QAbstractSocket to change the return value of the peerPort() method after a connection has been established. This feature is commonly used by proxy connections for virtual connection settings.
- See also
- peerPort(), setPeerAddress(), setLocalPort()
| void QAbstractSocket::setProxy | ( | const QNetworkProxy & | networkProxy | ) |
Sets the explicit network proxy for this socket to networkProxy.
To disable the use of a proxy for this socket, use the QNetworkProxy::NoProxy proxy type:
The default value for the proxy is QNetworkProxy::DefaultProxy, which means the socket will use the application settings: if a proxy is set with QNetworkProxy::setApplicationProxy, it will use that, otherwise if a factory is set with QNetworkProxyFactory::setApplicationProxyFactory, it will query that factory with type QNetworkProxyQuery::TcpSocket.
|
virtual |
Sets the size of QAbstractSocket's internal read buffer to be size bytes.
If the buffer size is limited to a certain size, QAbstractSocket will not buffer more than this size of data. Exceptionally, a buffer size of 0 means that the read buffer is unlimited and all incoming data is buffered. This is the default.
This option is useful if you only read the data at certain points in time (e.g., in a real-time streaming application) or if you want to protect your socket against receiving too much data, which may eventually cause your application to run out of memory.
Only QTcpSocket uses QAbstractSocket's internal buffer; QUdpSocket does not use any buffering at all, but rather relies on the implicit buffering provided by the operating system. Because of this, calling this method on QUdpSocket has no effect.
- See also
- readBufferSize(), read()
Reimplemented in QSslSocket::setReadBufferSize()
|
virtual |
Initializes QAbstractSocket with the native socket descriptor socketDescriptor. Returns true if socketDescriptor is accepted as a valid socket descriptor, otherwise returns false. The socket is opened in the mode specified by openMode, and enters the socket state specified by socketState.
- Note
- It is not possible to initialize two abstract sockets with the same native socket descriptor.
- See also
- socketDescriptor()
Reimplemented in QSslSocket::setSocketDescriptor()
|
protected |
Sets the type of error that last occurred to socketError.
- See also
- setSocketState(), setErrorString()
|
virtual |
Sets the given option to the value described by value.
- See also
- socketOption()
Reimplemented in QSslSocket::setSocketOption()
|
protected |
Sets the state of the socket to state.
- See also
- state()
|
virtual |
Returns the native socket descriptor of the QAbstractSocket object if this is available, otherwise returns -1.
If the socket is using QNetworkProxy, the returned descriptor may not be usable with native socket functions. The socket descriptor is not available when QAbstractSocket is in UnconnectedState.
- See also
- setSocketDescriptor()
|
virtual |
| SocketType QAbstractSocket::socketType | ( | ) | const |
Returns the socket type (TCP, UDP, or other).
- See also
- QTcpSocket, QUdpSocket
| SocketState QAbstractSocket::state | ( | ) | const |
Returns the state of the socket.
- See also
- error()
|
signal |
This signal is emitted whenever QAbstractSocket's state changes. The socketState parameter is the new state.
- See also
- state(), Creating Custom Types
|
overridevirtual |
Reimplemented from QIODevice::waitForBytesWritten()
Reimplemented in QSslSocket::waitForBytesWritten()
|
virtual |
Waits until the socket is connected, up to msecs milliseconds. If the connection has been established, this method returns true, otherwise it returns false. In the case where it returns false, you can call error() to determine the cause of the error.
The following example waits up to one second for a connection to be established:
If msecs is -1, this method will not time out.
- Note
- This method may wait slightly longer than msecs, depending on the time it takes to complete the host lookup.
- Multiple calls to this functions do not accumulate the time. If the method times out, the connecting process will be aborted.
- See also
- connectToHost(), connected()
Reimplemented in QSslSocket::waitForConnected()
|
virtual |
Waits until the socket has disconnected, up to msecs milliseconds. If the connection has been disconnected, this method returns true, otherwise it returns false. In the case where it returns false, you can call error() to determine the cause of the error.
The following example waits up to one second for a connection to be closed:
If msecs is -1, this method will not time out.
- See also
- disconnectFromHost(), close()
Reimplemented in QSslSocket::waitForDisconnected()
|
overridevirtual |
This method blocks until new data is available for reading and the readyRead() signal has been emitted. The method will timeout after msecs milliseconds; the default timeout is 30000 milliseconds.
The method returns true if the readyRead() signal is emitted and there is new data available for reading, otherwise it returns false (if an error occurred or the operation timed out).
- See also
- waitForBytesWritten()
Reimplemented from QIODevice::waitForReadyRead()
Reimplemented in QSslSocket::waitForReadyRead()
Implements QIODevice::writeData()
Reimplemented in QSslSocket::writeData()


