 |
CopperSpice API
2.1.0
|
The QPainterPath class provides a container for painting operations, enabling graphical shapes to be constructed and reused. More...
Classes | |
| class | Element |
| Specifies the position and type of a subpath More... | |
Public Types | |
| enum | ElementType |
Public Methods | |
| QPainterPath () | |
| QPainterPath (const QPainterPath &other) | |
| QPainterPath (const QPointF &startPoint) | |
| ~QPainterPath () | |
| void | addEllipse (const QPointF ¢er, qreal rx, qreal ry) |
| void | addEllipse (const QRectF &rect) |
| void | addEllipse (qreal x, qreal y, qreal width, qreal height) |
| void | addPath (const QPainterPath &path) |
| void | addPolygon (const QPolygonF &polygon) |
| void | addRect (const QRectF &rect) |
| void | addRect (qreal x, qreal y, qreal width, qreal height) |
| void | addRegion (const QRegion ®ion) |
| void | addRoundedRect (const QRectF &rect, qreal xRadius, qreal yRadius, Qt::SizeMode mode=Qt::AbsoluteSize) |
| void | addRoundedRect (qreal x, qreal y, qreal width, qreal height, qreal xRadius, qreal yRadius, Qt::SizeMode mode=Qt::AbsoluteSize) |
| void | addRoundRect (const QRectF &rect, int roundness) |
| void | addRoundRect (const QRectF &rect, int xRound, int yRound) |
| void | addRoundRect (qreal x, qreal y, qreal width, qreal height, int roundness) |
| void | addRoundRect (qreal x, qreal y, qreal width, qreal height, int xRound, int yRound) |
| void | addText (const QPointF &point, const QFont &font, const QString &text) |
| void | addText (qreal x, qreal y, const QFont &font, const QString &text) |
| qreal | angleAtPercent (qreal t) const |
| void | arcMoveTo (const QRectF &rect, qreal angle) |
| void | arcMoveTo (qreal x, qreal y, qreal width, qreal height, qreal angle) |
| void | arcTo (const QRectF &rect, qreal startAngle, qreal arcLength) |
| void | arcTo (qreal x, qreal y, qreal width, qreal height, qreal startAngle, qreal arcLength) |
| QRectF | boundingRect () const |
| void | closeSubpath () |
| void | connectPath (const QPainterPath &path) |
| bool | contains (const QPainterPath &other) const |
| bool | contains (const QPointF &point) const |
| bool | contains (const QRectF &rect) const |
| QRectF | controlPointRect () const |
| void | cubicTo (const QPointF &point1, const QPointF &point2, const QPointF &point3) |
| void | cubicTo (qreal x1, qreal y1, qreal x2, qreal y2, qreal x3, qreal y3) |
| QPointF | currentPosition () const |
| QPainterPath::Element | elementAt (int index) const |
| int | elementCount () const |
| Qt::FillRule | fillRule () const |
| QPainterPath | intersected (const QPainterPath &other) const |
| bool | intersects (const QPainterPath &other) const |
| bool | intersects (const QRectF &rect) const |
| bool | isEmpty () const |
| qreal | length () const |
| void | lineTo (const QPointF &endPoint) |
| void | lineTo (qreal x, qreal y) |
| void | moveTo (const QPointF &point) |
| void | moveTo (qreal x, qreal y) |
| bool | operator!= (const QPainterPath &other) const |
| QPainterPath | operator& (const QPainterPath &other) const |
| QPainterPath & | operator&= (const QPainterPath &other) |
| QPainterPath | operator+ (const QPainterPath &other) const |
| QPainterPath & | operator+= (const QPainterPath &other) |
| QPainterPath | operator- (const QPainterPath &other) const |
| QPainterPath & | operator-= (const QPainterPath &other) |
| QPainterPath & | operator= (const QPainterPath &other) |
| QPainterPath & | operator= (QPainterPath &&other) |
| bool | operator== (const QPainterPath &other) const |
| QPainterPath | operator| (const QPainterPath &other) const |
| QPainterPath & | operator|= (const QPainterPath &other) |
| qreal | percentAtLength (qreal len) const |
| QPointF | pointAtPercent (qreal t) const |
| void | quadTo (const QPointF &point1, const QPointF &point2) |
| void | quadTo (qreal x1, qreal y1, qreal x2, qreal y2) |
| void | setElementPositionAt (int index, qreal x, qreal y) |
| void | setFillRule (Qt::FillRule fillRule) |
| QPainterPath | simplified () const |
| qreal | slopeAtPercent (qreal t) const |
| QPainterPath | subtracted (const QPainterPath &other) const |
| QPainterPath | subtractedInverted (const QPainterPath &other) const |
| void | swap (QPainterPath &other) |
| QPolygonF | toFillPolygon (const QMatrix &matrix=QMatrix ()) const |
| QPolygonF | toFillPolygon (const QTransform &matrix) const |
| QList< QPolygonF > | toFillPolygons (const QMatrix &matrix=QMatrix ()) const |
| QList< QPolygonF > | toFillPolygons (const QTransform &matrix) const |
| QPainterPath | toReversed () const |
| QList< QPolygonF > | toSubpathPolygons (const QMatrix &matrix=QMatrix ()) const |
| QList< QPolygonF > | toSubpathPolygons (const QTransform &matrix) const |
| void | translate (const QPointF &offset) |
| void | translate (qreal dx, qreal dy) |
| QPainterPath | translated (const QPointF &offset) const |
| QPainterPath | translated (qreal dx, qreal dy) const |
| QPainterPath | united (const QPainterPath &other) const |
Friends | |
| QDataStream & | operator<< (QDataStream &stream, const QPainterPath &path) |
| QDataStream & | operator>> (QDataStream &stream, QPainterPath &path) |
| class | QMatrix |
| class | QPainterPathStroker |
| class | QTransform |
Detailed Description
The QPainterPath class provides a container for painting operations, enabling graphical shapes to be constructed and reused.
A painter path is an object composed of a number of graphical building blocks, such as rectangles, ellipses, lines, and curves. Building blocks can be joined in closed subpaths, for example as a rectangle or an ellipse. A closed path has coinciding start and end points. Or they can exist independently as unclosed subpaths, such as lines and curves.
A QPainterPath object can be used for filling, outlining, and clipping. To generate fillable outlines for a given painter path, use the QPainterPathStroker class. The main advantage of painter paths over normal drawing operations is that complex shapes only need to be created once; then they can be drawn many times using only calls to the QPainter::drawPath() method.
QPainterPath provides a collection of methods that can be used to obtain information about the path and its elements. In addition it is possible to reverse the order of the elements using the toReversed() method. There are also several methods to convert this painter path object into a polygon representation.
Composing a QPainterPath
A QPainterPath object can be constructed as an empty path, with a given start point, or as a copy of another QPainterPath object. Once created, lines and curves can be added to the path using the lineTo(), arcTo(), cubicTo() and quadTo() methods. The lines and curves stretch from the currentPosition() to the position passed as argument.
The currentPosition() of the QPainterPath object is always the end position of the last subpath that was added (or the initial start point). Use the moveTo() method to move the currentPosition() without adding a component. The moveTo() method implicitly starts a new subpath, and closes the previous one. Another way of starting a new subpath is to call the closeSubpath() method which closes the current path by adding a line from the currentPosition() back to the path's start position. Note that the new path will have (0, 0) as its initial currentPosition().
QPainterPath class also provides several methods to add closed subpaths to a painter path: addEllipse(), addPath(), addRect(), addRegion() and addText(). The addPolygon() method adds an unclosed subpath. In fact, these methods are all collections of moveTo(), lineTo() and cubicTo() operations.
In addition, a path can be added to the current path using the connectPath() method. But note that this method will connect the last element of the current path to the first element of given one by adding a line.
The following code shows how a QPainterPath object can be used.
 | QPainterPath path;
path.addRect(20, 20, 60, 60);
path.moveTo(0, 0);
path.cubicTo(99, 0, 50, 50, 99, 99);
path.cubicTo(0, 99, 50, 50, 0, 0);
QPainter painter(this);
painter.fillRect(0, 0, 100, 100, Qt::white);
Qt::FlatCap, Qt::MiterJoin));
painter.drawPath(path);
|
The painter path is initially empty when constructed. We first add a rectangle, which is a closed subpath. Then we add two bezier curves which together form a closed subpath even though they are not closed individually. Finally we draw the entire path. The path is filled using the default fill rule, Qt::OddEvenFill. CopperSpice provides two methods for filling paths:
| Qt::OddEvenFill | Qt::WindingFill |
|---|---|
 |  |
Refer to the Qt::FillRule documentation for the definition of the rules. A painter path's currently set fill rule can be retrieved using the fillRule() method, and altered using the setFillRule() method.
QPainterPath Information
The QPainterPath class provides a collection of methods that returns information about the path and its elements.
The currentPosition() method returns the end point of the last subpath that was added (or the initial start point). The elementAt() method can be used to retrieve the various subpath elements, the number of elements can be retrieved using the elementCount() method, and the isEmpty() method tells whether this QPainterPath object contains any elements at all.
The controlPointRect() method returns the rectangle containing all the points and control points in this path. This method is significantly faster to compute than the exact boundingRect() which returns the bounding rectangle of this painter path with floating point precision.
Finally, QPainterPath provides the contains() method which can be used to determine whether a given point or rectangle is inside the path, and the intersects() method which determines if any of the points inside a given rectangle also are inside this path.
QPainterPath Conversion
For compatibility reasons, it might be required to simplify the representation of a painter path: QPainterPath provides the toFillPolygon(), toFillPolygons() and toSubpathPolygons() methods which convert the painter path into a polygon. The toFillPolygon() returns the painter path as one single polygon, while the two latter methods return a list of polygons.
The toFillPolygons() and toSubpathPolygons() methods are provided because it is usually faster to draw several small polygons than to draw one large polygon, even though the total number of points drawn is the same. The difference between the two is the number of polygons they return: The toSubpathPolygons() creates one polygon for each subpath regardless of intersecting subpaths (i.e. overlapping bounding rectangles), while the toFillPolygons() methods creates only one polygon for overlapping subpaths.
The toFillPolygon() and toFillPolygons() methods first convert all the subpaths to polygons, then uses a rewinding technique to make sure that overlapping subpaths can be filled using the correct fill rule. Note that rewinding inserts additional lines in the polygon so the outline of the fill polygon does not match the outline of the path.
- See also
- QPainterPathStroker, QPainter, QRegion
Member Enumeration Documentation
This enum describes the types of elements used to connect vertices in subpaths.
Elements added as closed subpaths using the addEllipse(), addPath(), addPolygon(), addRect(), addRegion() and addText() methods, is actually added to the path as a collection of separate elements using the moveTo(), lineTo() and cubicTo() methods.
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
QPainterPath::MoveToElement | 0 | A new subpath. Refer to moveTo(). |
QPainterPath::LineToElement | 1 | A line. Refer to lineTo(). |
QPainterPath::CurveToElement | 2 | A curve. Refer to cubicTo() and quadTo(). |
QPainterPath::CurveToDataElement | 3 | The extra data required to describe a curve in a CurveToElement element. |
- See also
- elementAt(), elementCount()
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
| QPainterPath::QPainterPath | ( | ) |
Constructs an empty QPainterPath object.
|
explicit |
Creates a QPainterPath object with the given startPoint as its current position.
| QPainterPath::QPainterPath | ( | const QPainterPath & | other | ) |
Copy constructs a new QPainterPath from other.
- See also
- operator=()
| QPainterPath::~QPainterPath | ( | ) |
Destroys this QPainterPath object.
Method Documentation
Creates an ellipse positioned at center with radii rx and ry, and adds it to the painter path as a closed subpath.
| void QPainterPath::addEllipse | ( | const QRectF & | rect | ) |
Creates an ellipse within the specified rect and adds it to the painter path as a closed subpath. The ellipse is composed of a clockwise curve, starting and finishing at zero degrees (the 3 o'clock position).
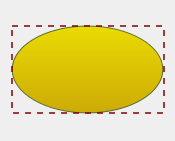 | QLinearGradient myGradient;
QPen myPen;
QRectF boundingRectangle;
QPainterPath myPath;
myPath.addEllipse(boundingRectangle);
QPainter painter(this);
painter.setBrush(myGradient);
painter.setPen(myPen);
painter.drawPath(myPath);
|
- See also
- arcTo(), QPainter::drawEllipse()
Creates an ellipse within the bounding rectangle defined by its top-left corner at (x, y), width and height, and adds it to the painter path as a closed subpath.
| void QPainterPath::addPath | ( | const QPainterPath & | path | ) |
Adds the given path to the current QPainterPath as a closed subpath.
- See also
- connectPath()
| void QPainterPath::addPolygon | ( | const QPolygonF & | polygon | ) |
Adds the given polygon to the path as an (unclosed) subpath. The current position after the polygon has been added, is the last point in polygon. To draw a line back to the first point, use the closeSubpath() method.
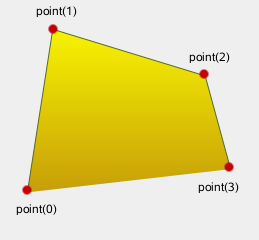 | QLinearGradient myGradient;
QPen myPen;
QPolygonF myPolygon;
QPainterPath myPath;
myPath.addPolygon(myPolygon);
QPainter painter(this);
painter.setBrush(myGradient);
painter.setPen(myPen);
painter.drawPath(myPath);
|
- See also
- lineTo()
| void QPainterPath::addRect | ( | const QRectF & | rect | ) |
Adds the given rect to this path as a closed subpath. The rectangle is added as a clockwise set of lines. The painter path's current position after the rectangle has been added is at the top-left corner of the rectangle.
 | QLinearGradient myGradient;
QPen myPen;
QRectF myRectangle;
QPainterPath myPath;
myPath.addRect(myRectangle);
QPainter painter(this);
painter.setBrush(myGradient);
painter.setPen(myPen);
painter.drawPath(myPath);
|
- See also
- addRegion(), lineTo()
Adds a rectangle at position (x, y), with the given width and height, as a closed subpath.
| void QPainterPath::addRegion | ( | const QRegion & | region | ) |
Adds the given region to the path by adding each rectangle in the region as a separate closed subpath.
- See also
- addRect()
| void QPainterPath::addRoundedRect | ( | const QRectF & | rect, |
| qreal | xRadius, | ||
| qreal | yRadius, | ||
| Qt::SizeMode | mode = Qt::AbsoluteSize |
||
| ) |
Adds the given rectangle rect with rounded corners to the path.
The xRadius and yRadius arguments specify the radii of the ellipses defining the corners of the rounded rectangle. When mode is Qt::RelativeSize, xRadius and yRadius are specified in percentage of half the rectangle's width and height respectively, and should be in the range 0.0 to 100.0.
- See also
- addRect()
|
inline |
Adds the given rectangle x, y, width, height with rounded corners to the path.
|
inlinedeprecated |
Adds a rounded rectangle, rect, to the path.
The roundness argument specifies uniform roundness for the rectangle. Vertical and horizontal roundness factors will be adjusted accordingly to act uniformly around both axes. Use this method if you want a rectangle equally rounded across both the X and Y axis.
- See also
- addRoundedRect()
|
deprecated |
- Deprecated:
- Adds a rectangle rect with rounded corners to the path.
The xRound and yRound arguments specify how rounded the corners should be. 0 is angled corners, 99 is maximum roundedness.
- See also
- addRoundedRect()
|
inlinedeprecated |
Adds a rounded rectangle to the path, defined by the coordinates x and y with the specified width and height.
The roundness argument specifies uniform roundness for the rectangle. Vertical and horizontal roundness factors will be adjusted accordingly to act uniformly around both axes. Use this method if you want a rectangle equally rounded across both the X and Y axis.
- See also
- addRoundedRect()
|
inlinedeprecated |
Adds a rectangle with rounded corners to the path. The rectangle is constructed from x, y, and the width and height width and height. The xRound and yRound arguments specify how rounded the corners should be. 0 is angled corners, 99 is maximum roundedness.
- See also
- addRoundedRect()
Adds the given text to this path as a set of closed subpaths created from the font supplied. The subpaths are positioned so that the left end of the text's baseline lies at the specified point.
 | QLinearGradient myGradient;
QPen myPen;
QFont myFont;
QPointF baseline(x, y);
QPainterPath myPath;
myPath.addText(baseline, myFont, tr("CopperSpice"));
QPainter painter(this);
painter.setBrush(myGradient);
painter.setPen(myPen);
painter.drawPath(myPath);
|
- See also
- QPainter::drawText()
Adds the given text to this path as a set of closed subpaths created from the font supplied. The subpaths are positioned so that the left end of the text's baseline lies at the point specified by (x, y).
Returns the angle of the path tangent at the percentage t and it must be between 0 and 1. Positive values for the angles mean counter-clockwise while negative values mean the clockwise direction. Zero degrees is at the 3 o'clock position.
Note that similarly to the other percent methods, the percentage measurement is not linear with regards to the length if curves are present in the path. When curves are present the percentage argument is mapped to the t parameter of the Bezier equations.
Creates a move to that lies on the arc that occupies the QRectF(x, y, width, height) at angle.
Creates an arc that occupies the given rect beginning at the specified startAngle and extending arcLength degrees counter-clockwise. Angles are specified in degrees. Clockwise arcs can be specified using negative angles.
This method connects the starting point of the arc to the current position if they are not already connected. After the arc has been added, the current position is the last point in arc. To draw a line back to the first point, use the closeSubpath() method.
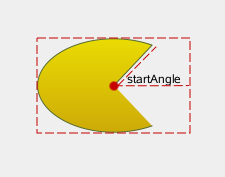 | QLinearGradient myGradient;
QPen myPen;
QPointF center, startPoint;
QPainterPath myPath;
myPath.moveTo(center);
myPath.arcTo(boundingRect, startAngle, sweepLength);
QPainter painter(this);
painter.setBrush(myGradient);
painter.setPen(myPen);
painter.drawPath(myPath);
|
|
inline |
Creates an arc that occupies the rectangle QRectF(x, y, width, height), beginning at the specified startAngle and extending arcLength degrees counter-clockwise.
| QRectF QPainterPath::boundingRect | ( | ) | const |
Returns the bounding rectangle of this painter path as a rectangle with floating point precision.
- See also
- controlPointRect()
| void QPainterPath::closeSubpath | ( | ) |
Closes the current subpath by drawing a line to the beginning of the subpath, automatically starting a new path. The current point of the new path is (0, 0). If the subpath does not contain any elements, this method does nothing.
- See also
- moveTo()
| void QPainterPath::connectPath | ( | const QPainterPath & | path | ) |
Connects the given path to the current QPainterPath by adding a line from the last element of this path to the first element of the given path.
- See also
- addPath()
| bool QPainterPath::contains | ( | const QPainterPath & | other | ) | const |
Returns true if the current QPainterPath completely contains other. Returns false if any edge of the current QPainterPath and other intersect.
Set operations on paths will treat the paths as areas. Non-closed paths will be treated as implicitly closed.
- See also
- intersects()
| bool QPainterPath::contains | ( | const QPointF & | point | ) | const |
Returns true if the given point is inside the path, otherwise returns false.
- See also
- intersects()
| bool QPainterPath::contains | ( | const QRectF & | rect | ) | const |
Returns true if the given rect is inside the path, otherwise returns false.
| QRectF QPainterPath::controlPointRect | ( | ) | const |
Returns the rectangle containing all the points and control points in this path. This method is significantly faster to compute than the exact boundingRect(), and the returned rectangle is always a superset of the rectangle returned by boundingRect().
- See also
- boundingRect()
| void QPainterPath::cubicTo | ( | const QPointF & | point1, |
| const QPointF & | point2, | ||
| const QPointF & | point3 | ||
| ) |
Adds a cubic Bezier curve between the current position and the given point3 using the control points specified by point1, and point2. After the curve is added, the current position is updated to be at the end point of the curve.
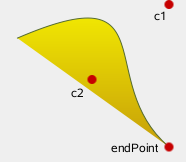 | QLinearGradient myGradient;
QPen myPen;
QPainterPath myPath;
myPath.cubicTo(point1, point2, point3);
QPainter painter(this);
painter.setBrush(myGradient);
painter.setPen(myPen);
painter.drawPath(myPath);
|
- See also
- quadTo()
Adds a cubic Bezier curve between the current position and the end point (x3, y3) with control points specified by (x1, y1) and (x2, y2).
| QPointF QPainterPath::currentPosition | ( | ) | const |
Returns the current position of the path.
| QPainterPath::Element QPainterPath::elementAt | ( | int | index | ) | const |
Returns the element at the given index in the painter path.
- See also
- ElementType, elementCount(), isEmpty()
| int QPainterPath::elementCount | ( | ) | const |
Returns the number of path elements in the painter path.
- See also
- ElementType, elementAt(), isEmpty()
| Qt::FillRule QPainterPath::fillRule | ( | ) | const |
Returns the painter path's currently set fill rule.
- See also
- setFillRule()
| QPainterPath QPainterPath::intersected | ( | const QPainterPath & | other | ) | const |
Returns a path which is the intersection of this path's fill area and the other fill area. Bezier curves may be flattened to line segments due to numerical instability of doing bezier curve intersections.
| bool QPainterPath::intersects | ( | const QPainterPath & | other | ) | const |
Returns true if the current QPainterPath intersects other at any point. This method will also return true if the current path overlaps any part of the other QPainterPath.
Set operations on paths will treat the paths as areas. Non-closed paths will be treated as implicitly closed.
- See also
- contains()
| bool QPainterPath::intersects | ( | const QRectF & | rect | ) | const |
Returns true if any point in the given rect intersects the path, otherwise returns false.
There is an intersection if any of the lines making up the rectangle crosses a part of the path or if any part of the rectangle overlaps with any area enclosed by the path. This method respects the current fillRule to determine what is considered inside the path.
- See also
- contains()
| bool QPainterPath::isEmpty | ( | ) | const |
Returns true if either there are no elements in this path, or if the only element is a MoveToElement, otherwise returns false.
- See also
- elementCount()
| qreal QPainterPath::length | ( | ) | const |
Returns the length of the current path.
| void QPainterPath::lineTo | ( | const QPointF & | endPoint | ) |
Adds a straight line from the current position to the given endPoint. After the line is drawn, the current position is updated to be at the end point of the line.
- See also
- addPolygon(), addRect()
Draws a line from the current position to the point (x, y).
| void QPainterPath::moveTo | ( | const QPointF & | point | ) |
Moves the current point to the given point, implicitly starting a new subpath and closing the previous one.
- See also
- closeSubpath()
Moves the current position to (x, y) and starts a new subpath, implicitly closing the previous path.
| bool QPainterPath::operator!= | ( | const QPainterPath & | other | ) | const |
Returns true if this painter path differs from the given other. Comparing paths may involve a per element comparison which can be slow for complex paths.
- See also
- operator==()
| QPainterPath QPainterPath::operator& | ( | const QPainterPath & | other | ) | const |
Returns the intersection of this path and the other path.
- See also
- intersected(), operator&=(), united(), operator|()
| QPainterPath & QPainterPath::operator&= | ( | const QPainterPath & | other | ) |
Intersects this path with other and returns a reference to this path.
- See also
- intersected(), operator&(), operator|=()
| QPainterPath QPainterPath::operator+ | ( | const QPainterPath & | other | ) | const |
Returns the union of this path and the other path. This method is equivalent to operator|().
- See also
- united(), operator+=(), operator-()
| QPainterPath & QPainterPath::operator+= | ( | const QPainterPath & | other | ) |
Unites this path with other, and returns a reference to this path. This is equivalent to operator|=().
- See also
- united(), operator+(), operator-=()
| QPainterPath QPainterPath::operator- | ( | const QPainterPath & | other | ) | const |
Subtracts the other path from a copy of this path and returns the copy.
- See also
- subtracted(), operator-=(), operator+()
| QPainterPath & QPainterPath::operator-= | ( | const QPainterPath & | other | ) |
Subtracts other from this path and returns a reference to this path.
- See also
- subtracted(), operator-(), operator+=()
| QPainterPath & QPainterPath::operator= | ( | const QPainterPath & | other | ) |
Copy assigns from other and returns a reference to this object.
- See also
- QPainterPath()
|
inline |
Move assigns from other and returns a reference to this object.
| bool QPainterPath::operator== | ( | const QPainterPath & | other | ) | const |
Returns true if this painterpath is equal to the given other. Comparing paths may involve a per element comparison which can be slow for complex paths.
- See also
- operator!=()
| QPainterPath QPainterPath::operator| | ( | const QPainterPath & | other | ) | const |
Returns the union of this path and the other path.
- See also
- united(), operator|=(), intersected(), operator&()
| QPainterPath & QPainterPath::operator|= | ( | const QPainterPath & | other | ) |
Unites this path with other and returns a reference to this path.
- See also
- united(), operator|(), operator&=()
Returns percentage of the whole path at the specified length len.
Note that similarly to other percent methods, the percentage measurement is not linear with regards to the length, if curves are present in the path. When curves are present the percentage argument is mapped to the t parameter of the Bezier equations.
Returns the point at the percentage t of the current path. The argument t must be between 0 and 1.
Similarly to other percent methods, the percentage measurement is not linear with regards to the length, if curves are present in the path. When curves are present the percentage argument is mapped to the t parameter of the Bezier equations.
Adds a quadratic Bezier curve between the current position and the given point2 with the control point specified by point1. After the curve is added, the current point is updated to be at the end point of the curve.
- See also
- cubicTo()
Adds a quadratic Bezier curve between the current point and the endpoint (x2, y2) with the control point specified by (x1, y1).
Sets the x and y coordinate of the element at index to x and y.
| void QPainterPath::setFillRule | ( | Qt::FillRule | fillRule | ) |
Sets the fill rule of the painter path to the given fillRule. CopperSpice provides two methods for filling paths.
| Qt::OddEvenFill (default) | Qt::WindingFill |
|---|---|
 |  |
- See also
- fillRule()
| QPainterPath QPainterPath::simplified | ( | ) | const |
Returns a simplified version of this path. This implies merging all subpaths that intersect, and returning a path containing no intersecting edges. Consecutive parallel lines will also be merged. The simplified path will always use the default fill rule, Qt::OddEvenFill. Bezier curves may be flattened to line segments due to numerical instability of doing bezier curve intersections.
Returns the slope of the path at the percentage t and this must be between 0 and 1.
The percentage measurement is not linear with regards to the length, if curves are present in the path. When curves are present the percentage argument is mapped to the t parameter of the Bezier equations.
| QPainterPath QPainterPath::subtracted | ( | const QPainterPath & | other | ) | const |
Returns a path which is other fill area subtracted from this path's fill area. Set operations on paths will treat the paths as areas. Non-closed paths will be treated as implicitly closed. Bezier curves may be flattened to line segments due to numerical instability of doing bezier curve intersections.
|
deprecated |
- Deprecated:
- Use subtracted() instead.
- See also
- subtracted()
|
inline |
Swaps painter path other with this painter path. This operation is very fast and never fails.
Converts the path into a polygon using the QTransform matrix and returns the polygon.
| QPolygonF QPainterPath::toFillPolygon | ( | const QTransform & | matrix | ) | const |
Converts the path into a polygon using the QTransform matrix, and returns the polygon. The polygon is created by first converting all subpaths to polygons, then using a rewinding technique to make sure that overlapping subpaths can be filled using the correct fill rule.
Rewinding inserts addition lines in the polygon so the outline of the fill polygon does not match the outline of the path.
- See also
- toSubpathPolygons(), toFillPolygons()
Converts the path into a polygon using the QTransform matrix, and returns the list.
| QList< QPolygonF > QPainterPath::toFillPolygons | ( | const QTransform & | matrix | ) | const |
Converts the path into a list of polygons using the QTransform matrix and returns the list.
The method differs from the toFillPolygon() method in that it creates several polygons. It is provided because it is usually faster to draw several small polygons than to draw one large polygon, even though the total number of points drawn is the same.
The toFillPolygons() method differs from the toSubpathPolygons() method in that it create only polygon for subpaths that have overlapping bounding rectangles.
Like toFillPolygon(), this method uses a rewinding technique to make sure that overlapping subpaths can be filled using the correct fill rule. Rewinding inserts addition lines in the polygons so the outline of the fill polygon does not match the outline of the path.
- See also
- toSubpathPolygons(), toFillPolygon()
| QPainterPath QPainterPath::toReversed | ( | ) | const |
Converts the path into a list of polygons using the QTransform matrix, and returns the list.
| QList< QPolygonF > QPainterPath::toSubpathPolygons | ( | const QTransform & | matrix | ) | const |
Converts the path into a list of polygons using the QTransform matrix, and returns the list.
This method creates one polygon for each subpath regardless of intersecting subpaths (i.e. overlapping bounding rectangles). To make sure that such overlapping subpaths are filled correctly, use the toFillPolygons() method instead.
- See also
- toFillPolygons(), toFillPolygon()
|
inline |
Translates all elements in the path by the given offset.
- See also
- translated()
Translates all elements in the path by (dx, dy).
- See also
- translated()
|
inline |
Returns a copy of the path that is translated by the given offset.
- See also
- translate()
Returns a copy of the path that is translated by (dx, dy).
- See also
- translate()
| QPainterPath QPainterPath::united | ( | const QPainterPath & | other | ) | const |
Returns a path which is the union of this QPainterPath fill area and the other fill area.
Set operations on paths will treat the paths as areas. Non-closed paths will be treated as implicitly closed. Bezier curves may be flattened to line segments due to numerical instability of doing bezier curve intersections.
- See also
- intersected(), subtracted()
Friends And Related Function Documentation
|
friend |
Writes the path to the stream and returns a reference to the stream.
Refer to Serializing Data Types for additional information.
|
friend |
Reads the painter path from the stream into the specified path and returns a reference to the stream.
Refer to Serializing Data Types for additional information.


