 |
CopperSpice API
2.1.0
|
Base class for all graphical items in a QGraphicsScene. More...
Public Typedefs | |
| using | GraphicsItemFlags = QFlags< GraphicsItemFlag > |
Public Types | |
| enum | CacheMode |
| enum | GraphicsItemChange |
| enum | GraphicsItemFlag |
| enum | PanelModality |
Public Methods | |
| QGraphicsItem (QGraphicsItem *parent=nullptr) | |
| virtual | ~QGraphicsItem () |
| bool | acceptDrops () const |
| Qt::MouseButtons | acceptedMouseButtons () const |
| bool | acceptHoverEvents () const |
| bool | acceptTouchEvents () const |
| virtual void | advance (int phase) |
| virtual QRectF | boundingRect () const = 0 |
| QRegion | boundingRegion (const QTransform &itemToDeviceTransform) const |
| qreal | boundingRegionGranularity () const |
| CacheMode | cacheMode () const |
| QList< QGraphicsItem * > | childItems () const |
| QRectF | childrenBoundingRect () const |
| void | clearFocus () |
| QPainterPath | clipPath () const |
| virtual bool | collidesWithItem (const QGraphicsItem *graphicsItem, Qt::ItemSelectionMode mode=Qt::IntersectsItemShape) const |
| virtual bool | collidesWithPath (const QPainterPath &path, Qt::ItemSelectionMode mode=Qt::IntersectsItemShape) const |
| QList< QGraphicsItem * > | collidingItems (Qt::ItemSelectionMode mode=Qt::IntersectsItemShape) const |
| QGraphicsItem * | commonAncestorItem (const QGraphicsItem *graphicsItem) const |
| virtual bool | contains (const QPointF &point) const |
| QCursor | cursor () const |
| QVariant | data (int key) const |
| QTransform | deviceTransform (const QTransform &viewportTransform) const |
| qreal | effectiveOpacity () const |
| void | ensureVisible (const QRectF &rectF=QRectF (), int xmargin=50, int ymargin=50) |
| void | ensureVisible (qreal x, qreal y, qreal width, qreal height, int xmargin=50, int ymargin=50) |
| bool | filtersChildEvents () const |
| GraphicsItemFlags | flags () const |
| QGraphicsItem * | focusItem () const |
| QGraphicsItem * | focusProxy () const |
| void | grabKeyboard () |
| void | grabMouse () |
| QGraphicsEffect * | graphicsEffect () const |
| QGraphicsItemGroup * | group () const |
| bool | handlesChildEvents () const |
| bool | hasCursor () const |
| bool | hasFocus () const |
| void | hide () |
| Qt::InputMethodHints | inputMethodHints () const |
| void | installSceneEventFilter (QGraphicsItem *filterItem) |
| bool | isActive () const |
| bool | isAncestorOf (const QGraphicsItem *graphicsItem) const |
| bool | isBlockedByModalPanel (QGraphicsItem **blockingPanel=nullptr) const |
| bool | isClipped () const |
| bool | isEnabled () const |
| bool | isObscured (const QRectF &rectF=QRectF ()) const |
| bool | isObscured (qreal x, qreal y, qreal width, qreal height) const |
| virtual bool | isObscuredBy (const QGraphicsItem *graphicsItem) const |
| bool | isPanel () const |
| bool | isSelected () const |
| bool | isUnderMouse () const |
| bool | isVisible () const |
| bool | isVisibleTo (const QGraphicsItem *graphicsItem) const |
| bool | isWidget () const |
| bool | isWindow () const |
| QTransform | itemTransform (const QGraphicsItem *graphicsItem, bool *ok=nullptr) const |
| QPainterPath | mapFromItem (const QGraphicsItem *graphicsItem, const QPainterPath &path) const |
| QPointF | mapFromItem (const QGraphicsItem *graphicsItem, const QPointF &point) const |
| QPolygonF | mapFromItem (const QGraphicsItem *graphicsItem, const QPolygonF &polygon) const |
| QPolygonF | mapFromItem (const QGraphicsItem *graphicsItem, const QRectF &rectF) const |
| QPointF | mapFromItem (const QGraphicsItem *graphicsItem, qreal x, qreal y) const |
| QPolygonF | mapFromItem (const QGraphicsItem *graphicsItem, qreal x, qreal y, qreal width, qreal height) const |
| QPainterPath | mapFromParent (const QPainterPath &path) const |
| QPointF | mapFromParent (const QPointF &point) const |
| QPolygonF | mapFromParent (const QPolygonF &polygon) const |
| QPolygonF | mapFromParent (const QRectF &rectF) const |
| QPointF | mapFromParent (qreal x, qreal y) const |
| QPolygonF | mapFromParent (qreal x, qreal y, qreal width, qreal height) const |
| QPainterPath | mapFromScene (const QPainterPath &path) const |
| QPointF | mapFromScene (const QPointF &point) const |
| QPolygonF | mapFromScene (const QPolygonF &polygon) const |
| QPolygonF | mapFromScene (const QRectF &rectF) const |
| QPointF | mapFromScene (qreal x, qreal y) const |
| QPolygonF | mapFromScene (qreal x, qreal y, qreal width, qreal height) const |
| QRectF | mapRectFromItem (const QGraphicsItem *graphicsItem, const QRectF &rectF) const |
| QRectF | mapRectFromItem (const QGraphicsItem *graphicsItem, qreal x, qreal y, qreal width, qreal height) const |
| QRectF | mapRectFromParent (const QRectF &rectF) const |
| QRectF | mapRectFromParent (qreal x, qreal y, qreal width, qreal height) const |
| QRectF | mapRectFromScene (const QRectF &rectF) const |
| QRectF | mapRectFromScene (qreal x, qreal y, qreal width, qreal height) const |
| QRectF | mapRectToItem (const QGraphicsItem *graphicsItem, const QRectF &rectF) const |
| QRectF | mapRectToItem (const QGraphicsItem *graphicsItem, qreal x, qreal y, qreal width, qreal height) const |
| QRectF | mapRectToParent (const QRectF &rectF) const |
| QRectF | mapRectToParent (qreal x, qreal y, qreal width, qreal height) const |
| QRectF | mapRectToScene (const QRectF &rectF) const |
| QRectF | mapRectToScene (qreal x, qreal y, qreal width, qreal height) const |
| QPainterPath | mapToItem (const QGraphicsItem *graphicsItem, const QPainterPath &path) const |
| QPointF | mapToItem (const QGraphicsItem *graphicsItem, const QPointF &point) const |
| QPolygonF | mapToItem (const QGraphicsItem *graphicsItem, const QPolygonF &polygon) const |
| QPolygonF | mapToItem (const QGraphicsItem *graphicsItem, const QRectF &rectF) const |
| QPointF | mapToItem (const QGraphicsItem *graphicsItem, qreal x, qreal y) const |
| QPolygonF | mapToItem (const QGraphicsItem *graphicsItem, qreal x, qreal y, qreal width, qreal height) const |
| QPainterPath | mapToParent (const QPainterPath &path) const |
| QPointF | mapToParent (const QPointF &point) const |
| QPolygonF | mapToParent (const QPolygonF &polygon) const |
| QPolygonF | mapToParent (const QRectF &rectF) const |
| QPointF | mapToParent (qreal x, qreal y) const |
| QPolygonF | mapToParent (qreal x, qreal y, qreal width, qreal height) const |
| QPainterPath | mapToScene (const QPainterPath &path) const |
| QPointF | mapToScene (const QPointF &point) const |
| QPolygonF | mapToScene (const QPolygonF &polygon) const |
| QPolygonF | mapToScene (const QRectF &rectF) const |
| QPointF | mapToScene (qreal x, qreal y) const |
| QPolygonF | mapToScene (qreal x, qreal y, qreal width, qreal height) const |
| QMatrix | matrix () const |
| void | moveBy (qreal dx, qreal dy) |
| qreal | opacity () const |
| virtual QPainterPath | opaqueArea () const |
| virtual void | paint (QPainter *painter, const QStyleOptionGraphicsItem *option, QWidget *widget=nullptr) = 0 |
| QGraphicsItem * | panel () const |
| PanelModality | panelModality () const |
| QGraphicsItem * | parentItem () const |
| QGraphicsObject * | parentObject () const |
| QGraphicsWidget * | parentWidget () const |
| QPointF | pos () const |
| void | removeSceneEventFilter (QGraphicsItem *filterItem) |
| void | resetMatrix () |
| void | resetTransform () |
| qreal | rotation () const |
| qreal | scale () const |
| QGraphicsScene * | scene () const |
| QRectF | sceneBoundingRect () const |
| QMatrix | sceneMatrix () const |
| QPointF | scenePos () const |
| QTransform | sceneTransform () const |
| void | scroll (qreal dx, qreal dy, const QRectF &rectF=QRectF ()) |
| void | setAcceptDrops (bool on) |
| void | setAcceptedMouseButtons (Qt::MouseButtons buttons) |
| void | setAcceptHoverEvents (bool enabled) |
| void | setAcceptTouchEvents (bool enabled) |
| void | setActive (bool active) |
| void | setBoundingRegionGranularity (qreal granularity) |
| void | setCacheMode (CacheMode mode, const QSize &cacheSize=QSize ()) |
| void | setCursor (const QCursor &cursor) |
| void | setData (int key, const QVariant &value) |
| void | setEnabled (bool enabled) |
| void | setFiltersChildEvents (bool enabled) |
| void | setFlag (GraphicsItemFlag flag, bool enabled=true) |
| void | setFlags (GraphicsItemFlags flags) |
| void | setFocus (Qt::FocusReason focusReason=Qt::OtherFocusReason) |
| void | setFocusProxy (QGraphicsItem *graphicsItem) |
| void | setGraphicsEffect (QGraphicsEffect *effect) |
| void | setGroup (QGraphicsItemGroup *group) |
| void | setHandlesChildEvents (bool enabled) |
| void | setInputMethodHints (Qt::InputMethodHints hints) |
| void | setMatrix (const QMatrix &matrix, bool combine=false) |
| void | setOpacity (qreal opacity) |
| void | setPanelModality (PanelModality panelModality) |
| void | setParentItem (QGraphicsItem *parent) |
| void | setPos (const QPointF &pos) |
| void | setPos (qreal x, qreal y) |
| void | setRotation (qreal angle) |
| void | setScale (qreal factor) |
| void | setSelected (bool selected) |
| void | setToolTip (const QString &toolTip) |
| void | setTransform (const QTransform &matrix, bool combine=false) |
| void | setTransformations (const QList< QGraphicsTransform * > &transformations) |
| void | setTransformOriginPoint (const QPointF &origin) |
| void | setTransformOriginPoint (qreal x, qreal y) |
| void | setVisible (bool visible) |
| void | setX (qreal x) |
| void | setY (qreal y) |
| void | setZValue (qreal z) |
| virtual QPainterPath | shape () const |
| void | show () |
| void | stackBefore (const QGraphicsItem *graphicsItem) |
| QGraphicsObject * | toGraphicsObject () |
| const QGraphicsObject * | toGraphicsObject () const |
| QString | toolTip () const |
| QGraphicsItem * | topLevelItem () const |
| QGraphicsWidget * | topLevelWidget () const |
| QTransform | transform () const |
| QList< QGraphicsTransform * > | transformations () const |
| QPointF | transformOriginPoint () const |
| virtual int | type () const |
| void | ungrabKeyboard () |
| void | ungrabMouse () |
| void | unsetCursor () |
| void | update (const QRectF &rectF=QRectF ()) |
| void | update (qreal x, qreal y, qreal width, qreal height) |
| QGraphicsWidget * | window () const |
| qreal | x () const |
| qreal | y () const |
| qreal | zValue () const |
Static Public Members | |
| static constexpr const int | UserType = 65536 |
Friends | |
| class | QGraphicsItemGroup |
| class | QGraphicsObject |
| class | QGraphicsScene |
| class | QGraphicsView |
| class | QGraphicsWidget |
Related Functions | |
These are not member functions | |
| T | qgraphicsitem_cast (QGraphicsItem *item) |
Detailed Description
The QGraphicsItem class is the base class for all graphical items in a QGraphicsScene. This class is used to define the geometry, collision detection, painting implementation and item interaction through event handlers. It is part of the Graphics View System.
CopperSpice provides a set of standard graphic items for the common shapes.
- QGraphicsEllipseItem provides an ellipse item
- QGraphicsLineItem provides a line item
- QGraphicsPathItem provides an arbitrary path item
- QGraphicsPixmapItem provides a pixmap item
- QGraphicsPolygonItem provides a polygon item
- QGraphicsRectItem provides a rectangular item
- QGraphicsSimpleTextItem provides a simple text label item
- QGraphicsTextItem provides an advanced text browser item
The geometric information for an item is based on a local coordinate system. The position of the item can be obtained by calling pos(). The value of the position is relative to the parent coordinates. The Graphics View Coordinate System describes the coordinate system in detail.
Calling the setVisible() methods controls whether an item is drawn on the screen and can receive events. Hiding an item will also hide all of its children. An item can be enabled or disabled by calling setEnabled(). If you disable an item all its children will be disabled. By default graphic items are both visible and enabled.
To toggle whether an item is selected first set the ItemIsSelectable flag, then call setSelected(). The graphic item can also be selected by user interaction.
Custom Graphic Item
To create a custom graphic item, the first step is to subclass QGraphicsItem and then implement the following two methods: boundingRect(), which returns an estimate of the area painted by the item and paint(), which implements the actual painting.
The boundingRect() method has multiple purposes. QGraphicsScene bases its item index on boundingRect(), and QGraphicsView uses it both for culling invisible items, and for determining the area that needs to be recomposed when drawing overlapping items. In addition, QGraphicsItem's collision detection mechanisms use boundingRect() to provide an efficient cut-off. The fine grained collision algorithm in collidesWithItem() is based on calling shape(), which returns an accurate outline of the item's shape as a QPainterPath.
QGraphicsScene expects all items boundingRect() and shape() to remain unchanged unless it is notified. If you want to change an item's geometry in any way, you must first call prepareGeometryChange() to allow QGraphicsScene to update its bookkeeping.
Collision detection can be done in two ways:
- Reimplement shape() to return an accurate shape for your item, and rely on the default implementation of collidesWithItem() to do shape-shape intersection. This can be rather expensive if the shapes are complex
- Reimplement collidesWithItem() to provide your own custom item and shape collision algorithm
The contains() method can be called to determine whether the item contains a point or not. This method can also be reimplemented by the item. The default behavior of contains() is based on calling shape().
Items can contain other items, and also be contained by other items. All items can have a parent item and a list of children. Unless the item has no parent, its position is in parent coordinates. Parent items propagate both their position and their transformation to all children.
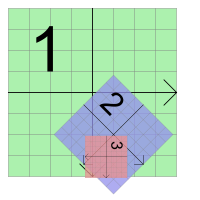
Transformations
QGraphicsItem supports projective transformations in addition to its base position, pos(). There are several ways to change an item's transformation. For simple transformations, you can call the methods setRotation() or setScale(), or you can pass any transformation matrix to setTransform(). For advanced transformation control you also have the option of setting several combined transformations by calling setTransformations().
Item transformations accumulate from parent to child, so if both a parent and child item are rotated 90 degrees, the child's total transformation will be 180 degrees. Similarly, if the item's parent is scaled to 2x its original size, its children will also be twice as large. An item's transformation does not affect its own local geometry, all geometry methods still operate in local coordinates. QGraphicsItem provides the method sceneTransform() which returns the item's total transformation matrix, including its position and all parent positions and transformations. The scenePos() method returns its position in scene coordinates.
To reset an item's matrix call resetTransform().
Certain transformation operations produce a different outcome depending on the order in which they are applied. For example, if you scale a transform, and then rotate it, you may get a different result than if the transform was rotated first. However, the order you set the transformation properties on QGraphicsItem does not affect the resulting transformation.
QGraphicsItem always applies the properties in a fixed defined order.
- Base transform is applied using transform()
- Transformations list is applied in order using transformations()
- Rotation relative to its transform origin point using rotation() and transformOriginPoint()
- Scaling relative to its transform origin point using scale() and transformOriginPoint()
Painting
The paint() method is called by QGraphicsView to paint the item's contents. The item has no background or default fill of its own, whatever is behind the item will shine through all areas that are not explicitly painted in this method. You can call update() to schedule a repaint, optionally passing the rectangle that needs a repaint. Depending on whether or not the item is visible in a view, the item may or may not be repainted, there is no equivalent to QWidget::repaint() in QGraphicsItem.
Items are painted by the view, starting with the parent items and then drawing children, in ascending stacking order. You can set an item's stacking order by calling setZValue(), and test it by calling zValue(), where items with low z-values are painted before items with high z-values. Stacking order applies to sibling items, parents are always drawn before their children.
Sorting
All items are drawn in a defined, stable order, and this same order decides which items will receive mouse input first when you click on the scene. Normally you do not have to worry about sorting, as the items follow a "natural order", following the logical structure of the scene.
An item's children are stacked on top of the parent and sibling items are stacked by insertion order. If you add item A, and then B, then B will be on top of A. If you then add C, the stacking order will be A, then B, then C.
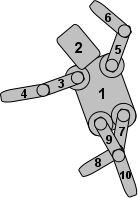
This example shows the stacking order of all limbs of the robot. The torso is the root item (all other items are children or descendants of the torso), so it is drawn first. Next, the head is drawn, as it is the first item in the torso's list of children. Then the upper left arm is drawn. As the lower arm is a child of the upper arm, the lower arm is then drawn, followed by the upper arm's next sibling, which is the upper right arm, and so on.
The z order can be modified in the following ways.
- Call setZValue() on an item to explicitly stack it on top of, or under, other sibling items
- Call stackBefore() to reorder the list of children. This will directly modify the insertion order
- Set the ItemStacksBehindParent flag to stack a child item behind its parent
The stacking order of two sibling items also applies to each item's children. If one graphic item A is on top of another item B, then all the children of A will be on top of all the children of B.
Events
QGraphicsItem receives events from QGraphicsScene through sceneEvent(). This method distributes the most common events to a set of event handlers.
- contextMenuEvent()
- handles context menu events
- focusInEvent(), focusOutEvent()
- handle focus in and out events
- hoverEnterEvent(), hoverMoveEvent(), hoverLeaveEvent()
- handles hover enter, move and leave events
- inputMethodEvent()
- handles input events, for accessibility support
- keyPressEvent(), keyReleaseEvent()
- handle key press and release events
- mousePressEvent(), mouseMoveEvent(), mouseReleaseEvent(), mouseDoubleClickEvent()
- handles mouse press, move, release, click and doubleclick events
You can filter events for any other item by installing scene event filters. This functionality is separate from the regular event filters which only work on subclasses of QObject. After installing your item as an event filter for another item by calling installSceneEventFilter(), the filtered events will be received by the method sceneEventFilter(). You can remove item event filters by calling removeSceneEventFilter().
Custom Data
To store custom data in a QGraphicsItem call setData() with a key-value pair. The key is an integer and the value is a QVariant. To retrieve the custom data from the QGraphicsItem call data().
- See also
- QGraphicsScene, QGraphicsView, Graphics View System
Member Typedef Documentation
Typedef for QFlags<GraphicsItemFlag> which contains an OR combination of GraphicsItemFlag values.
Refer to QGraphicsItem::GraphicsItemFlag for the enum documentation.
Member Enumeration Documentation
This enum describes QGraphicsItem's cache modes. Caching is used to speed up rendering by allocating and rendering to an off-screen pixel buffer, which can be reused when the item requires redrawing. For some paint devices, the cache is stored directly in graphics memory, which makes rendering efficient.
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
QGraphicsItem::NoCache | 0 | All item caching is disabled, default value. Method QGraphicsItem::paint() is called every time the item needs redrawing. |
QGraphicsItem::ItemCoordinateCache | 1 | Caching is enabled for the item's logical (local) coordinate system. QGraphicsItem creates an off-screen pixel buffer with a configurable size / resolution that you can pass to QGraphicsItem::setCacheMode(). Rendering quality will typically degrade, depending on the resolution of the cache and the item transformation. The first time the item is redrawn, it will render itself into the cache, and the cache is then reused for every subsequent expose. The cache is also reused as the item is transformed. To adjust the resolution of the cache, you can call setCacheMode() again. |
QGraphicsItem::DeviceCoordinateCache | 2 | Caching is enabled at the paint device level, in device coordinates. This mode is for items that can move, but are not rotated, scaled or sheared. If the item is transformed directly or indirectly, the cache will be regenerated automatically. Unlike ItemCoordinateCacheMode, DeviceCoordinateCache always renders at maximum quality. |
- See also
- QGraphicsItem::setCacheMode()
This enum describes the state changes that are notified by QGraphicsItem::itemChange(). The notifications are sent as the state changes, and in some cases, adjustments can be made. Be cautious when calling methods inside itemChange(). Certain methods can cause unwanted recursion. For example, you can not call setPos() in itemChange() on an ItemPositionChange notification, as the setPos() method will then call itemChange(ItemPositionChange). Instead, return the new, adjusted position from itemChange().
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
QGraphicsItem::ItemEnabledChange | 3 | Enabled state has changed. If the item is presently enabled, it will become disabled, and vice versa. The value argument is the new enabled state (i.e., true or false). Do not call setEnabled() in itemChange() as this notification is delivered. Instead, you can return the new state from itemChange(). |
QGraphicsItem::ItemEnabledHasChanged | 13 | Enabled state has changed. The value argument is the new enabled state (i.e., true or false). Do not call setEnabled() in itemChange() as this notification is delivered. The return value is ignored. |
QGraphicsItem::ItemMatrixChange | 1 | Affine transformation matrix is changing. This value is obsolete, use ItemTransformChange instead. |
QGraphicsItem::ItemPositionChange | 0 | Position changed. This notification is sent if the ItemSendsGeometryChanges flag is enabled, and when the item's local position changes, relative to its parent (i.e., as a result of calling setPos() or moveBy()). The value argument is the new position (i.e., a QPointF). You can call pos() to get the original position. Do not call setPos() or moveBy() in itemChange() as this notification is delivered; instead, you can return the new, adjusted position from itemChange(). After this notification, QGraphicsItem immediately sends the ItemPositionHasChanged notification if the position changed. |
QGraphicsItem::ItemPositionHasChanged | 9 | Position changed. This notification is sent if the ItemSendsGeometryChanges flag is enabled, and after the item's local position, relative to its parent, has changed. The value argument is the new position (the same as pos()), and QGraphicsItem ignores the return value for this notification (i.e., a read-only notification). |
QGraphicsItem::ItemTransformChange | 8 | Transformation matrix changed. This notification is send if the ItemSendsGeometryChanges flag is enabled, and when the item's local transformation matrix changes (i.e., as a result of calling setTransform(). The value argument is the new matrix (i.e., a QTransform); to get the old matrix, call transform(). Do not call setTransform() or set any of the transformation properties in itemChange() as this notification is delivered; instead, you can return the new matrix from itemChange(). This notification is not sent if you change the transformation properties. |
QGraphicsItem::ItemTransformHasChanged | 10 | Transformation matrix has changed either because setTransform is called, or one of the transformation properties is changed. This notification is sent if the ItemSendsGeometryChanges flag is enabled, and after the item's local transformation matrix has changed. The value argument is the new matrix (same as transform()), and QGraphicsItem ignores the return value for this notification (i.e., a read-only notification). |
QGraphicsItem::ItemRotationChange | 28 | Rotation property changed. This notification is sent if the ItemSendsGeometryChanges flag is enabled, and when the item's rotation property changes (i.e., as a result of calling setRotation()). The value argument is the new rotation (i.e., a double); to get the old rotation, call rotation(). Do not call setRotation() in itemChange() as this notification is delivered; instead, you can return the new rotation from itemChange(). |
QGraphicsItem::ItemRotationHasChanged | 29 | Rotation property changed. This notification is sent if the ItemSendsGeometryChanges flag is enabled, and after the item's rotation property has changed. The value argument is the new rotation (i.e., a double), and QGraphicsItem ignores the return value for this notification (i.e., a read-only notification). Do not call setRotation() in itemChange() as this notification is delivered. |
QGraphicsItem::ItemScaleChange | 30 | Scale property changed. This notification is sent if the ItemSendsGeometryChanges flag is enabled, and when the item's scale property changes (i.e., as a result of calling setScale()). The value argument is the new scale (i.e., a double); to get the old scale, call scale(). Do not call setScale() in itemChange() as this notification is delivered; instead, you can return the new scale from itemChange(). |
QGraphicsItem::ItemScaleHasChanged | 31 | Scale property changed. This notification is sent if the ItemSendsGeometryChanges flag is enabled, and after the item's scale property has changed. The value argument is the new scale (i.e., a double), and QGraphicsItem ignores the return value for this notification (i.e., a read-only notification). Do not call setScale() in itemChange() as this notification is delivered. |
QGraphicsItem::ItemTransformOriginPointChange | 32 | Transform origin point property changed. This notification is sent if the ItemSendsGeometryChanges flag is enabled, and when the item's transform origin point property changes (i.e., as a result of calling setTransformOriginPoint()). The value argument is the new origin point (i.e., a QPointF); to get the old origin point, call transformOriginPoint(). Do not call setTransformOriginPoint() in itemChange() as this notification is delivered; instead, you can return the new transform origin point from itemChange(). |
QGraphicsItem::ItemTransformOriginPointHasChanged | 33 | Transform origin point property changed. This notification is sent if the ItemSendsGeometryChanges flag is enabled, and after the item's transform origin point property has changed. The value argument is the new origin point (i.e., a QPointF), and QGraphicsItem ignores the return value for this notification (i.e., a read-only notification). Do not call setTransformOriginPoint() in itemChange() as this notification is delivered. |
QGraphicsItem::ItemSelectedChange | 4 | Selected state changed. If the item is presently selected, it will become unselected, and vice versa. The value argument is the new selected state (i.e., true or false). Do not call setSelected() in itemChange() as this notification is delivered; instead, you can return the new selected state from itemChange(). |
QGraphicsItem::ItemSelectedHasChanged | 14 | Selected state changed. The value argument is the new selected state (i.e., true or false). Do not call setSelected() in itemChange() as this notification is delivered. The return value is ignored. |
QGraphicsItem::ItemVisibleChange | 2 | Visible state changed. If the item is presently visible, it will become invisible, and vice versa. The value argument is the new visible state (i.e., true or false). Do not call setVisible() in itemChange() as this notification is delivered; instead, you can return the new visible state from itemChange(). |
QGraphicsItem::ItemVisibleHasChanged | 12 | Visible state changed. The value argument is the new visible state (i.e., true or false). Do not call setVisible() in itemChange() as this notification is delivered. The return value is ignored. |
QGraphicsItem::ItemParentChange | 5 | The item's parent changes. The value argument is the new parent item (i.e., a QGraphicsItem pointer). Do not call setParentItem() in itemChange() as this notification is delivered; instead, you can return the new parent from itemChange(). |
QGraphicsItem::ItemParentHasChanged | 15 | Parent changed. The value argument is the new parent (i.e., a pointer to a QGraphicsItem). Do not call setParentItem() in itemChange() as this notification is delivered. The return value is ignored. |
QGraphicsItem::ItemChildAddedChange | 6 | Child added to this item. The value argument is the new child item (i.e., a QGraphicsItem pointer). Do not pass this item to any item's setParentItem() method as this notification is delivered. The return value is unused; you can not adjust anything in this notification. Note that the new child might not be fully constructed when this notification is sent; calling pure virtual methods on the child can lead to a crash. |
QGraphicsItem::ItemChildRemovedChange | 7 | Child removed from this item. The value argument is the child item that is about to be removed (i.e., a QGraphicsItem pointer). The return value is unused; you can not adjust anything in this notification. |
QGraphicsItem::ItemSceneChange | 11 | Item moved to a new scene. This notification is also sent when the item is added to its initial scene, and when it is removed. The item's scene() is the old scene (or 0 if the item has not been added to a scene yet). The value argument is the new scene (i.e., a QGraphicsScene pointer), or a null pointer if the item is removed from a scene. Do not override this change by passing this item to QGraphicsScene::addItem() as this notification is delivered; instead, you can return the new scene from itemChange(). Use this feature with caution; objecting to a scene change can quickly lead to unwanted recursion. |
QGraphicsItem::ItemSceneHasChanged | 16 | Scene has changed. The item's scene() is the new scene. This notification is also sent when the item is added to its initial scene, and when it is removed.The value argument is the new scene (i.e., a pointer to a QGraphicsScene). Do not call setScene() in itemChange() as this notification is delivered. The return value is ignored. |
QGraphicsItem::ItemCursorChange | 17 | Cursor changed. The value argument is the new cursor (i.e., a QCursor). Do not call setCursor() in itemChange() as this notification is delivered. Instead, you can return a new cursor from itemChange(). |
QGraphicsItem::ItemCursorHasChanged | 18 | Cursor changed. The value argument is the new cursor (i.e., a QCursor). Do not call setCursor() as this notification is delivered. The return value is ignored. |
QGraphicsItem::ItemToolTipChange | 19 | Tooltip changed. The value argument is the new tooltip (i.e., a QToolTip). Do not call setToolTip() in itemChange() as this notification is delivered. Instead, you can return a new tooltip from itemChange(). |
QGraphicsItem::ItemToolTipHasChanged | 20 | The item's tooltip has changed. The value argument is the new tooltip (i.e., a QToolTip). Do not call setToolTip() as this notification is delivered. The return value is ignored. |
QGraphicsItem::ItemFlagsChange | 21 | Flags changed. The value argument is the new flags (i.e., a quint32). Do not call setFlags() in itemChange() as this notification is delivered. Instead, you can return the new flags from itemChange(). |
QGraphicsItem::ItemFlagsHaveChanged | 22 | The item's flags have changed. The value argument is the new flags (i.e., a quint32). Do not call setFlags() in itemChange() as this notification is delivered. The return value is ignored. |
QGraphicsItem::ItemZValueChange | 23 | Z-value changed. The value argument is the new Z-value (i.e., a double). Do not call setZValue() in itemChange() as this notification is delivered. Instead, you can return a new Z-value from itemChange(). |
QGraphicsItem::ItemZValueHasChanged | 24 | The item's Z-value has changed. The value argument is the new Z-value (i.e., a double). Do not call setZValue() as this notification is delivered. The return value is ignored. |
QGraphicsItem::ItemOpacityChange | 25 | Opacity changed. The value argument is the new opacity (i.e., a double). Do not call setOpacity() in itemChange() as this notification is delivered. Instead, you can return a new opacity from itemChange(). |
QGraphicsItem::ItemOpacityHasChanged | 26 | The item's opacity has changed. The value argument is the new opacity (i.e., a double). Do not call setOpacity() as this notification is delivered. The return value is ignored. |
QGraphicsItem::ItemScenePositionHasChanged | 27 | Scene position changed. This notification is sent if the ItemSendsScenePositionChanges flag is enabled, and after the item's scene position has changed (i.e., the position or transformation of the item itself or the position or transformation of any ancestor has changed). The value argument is the new scene position (the same as scenePos()), and QGraphicsItem ignores the return value for this notification (i.e., a read-only notification). |
This enum describes different flags which can be used to enable or disable features for a given item. All flags are disabled by default.
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| QGraphicsItem::ItemIsMovable | 0x1 | Item supports interactive movement using the mouse. By clicking on the item and then dragging, the item will move together with the mouse cursor. If the item has children, all children are also moved. If the item is part of a selection, all selected items are also moved. |
| QGraphicsItem::ItemIsSelectable | 0x2 | Item supports selection. Enabling this feature will enable setSelected() to toggle selection for the item. It will also let the item be selected automatically as a result of calling QGraphicsScene::setSelectionArea(), by clicking on an item, or by using rubber band selection in QGraphicsView. |
| QGraphicsItem::ItemIsFocusable | 0x4 | Item supports keyboard input focus (i.e., it is an input item). Enabling this flag will allow the item to accept focus, which again allows the delivery of key events to QGraphicsItem::keyPressEvent() and QGraphicsItem::keyReleaseEvent(). |
| QGraphicsItem::ItemClipsToShape | 0x8 | Item clips to its own shape. The item cannot draw or receive mouse, tablet, drag and drop or hover events outside its shape. It is disabled by default. This behavior is enforced by QGraphicsView::drawItems() or QGraphicsScene::drawItems(). |
| QGraphicsItem::ItemClipsChildrenToShape | 0x10 | Item clips the painting of all its descendants to its own shape. Items that are either direct or indirect children of this item cannot draw outside this item's shape. By default, this flag is disabled; children can draw anywhere. This behavior is enforced by QGraphicsView::drawItems() or QGraphicsScene::drawItems(). If this flag is set you can still scale the item itself, and that scale transformation will influence the item's children. |
| QGraphicsItem::ItemIgnoresTransformations | 0x20 | Item ignores inherited transformations (i.e., its position is still anchored to its parent, but the parent or view rotation, zoom or shear transformations are ignored). This flag is useful for keeping text label items horizontal and unscaled, so they will still be readable if the view is transformed. When set, the item's view geometry and scene geometry will be maintained separately. You must call deviceTransform() to map coordinates and detect collisions in the view. By default, this flag is disabled. This flag is similar to ItemContainsChildrenInShape but in addition enforces the containment by clipping the children. |
| QGraphicsItem::ItemIgnoresParentOpacity | 0x40 | Item ignores its parent's opacity. The item's effective opacity is the same as its own; it does not combine with the parent's opacity. This flags allows your item to keep its absolute opacity even if the parent is semitransparent. |
| QGraphicsItem::ItemDoesntPropagateOpacityToChildren | 0x80 | The item does not propagate its opacity to its children. This flag allows you to create a semitransparent item that does not affect the opacity of its children. |
| QGraphicsItem::ItemStacksBehindParent | 0x100 | Item is stacked behind its parent. By default, child items are stacked on top of the parent item. But setting this flag, the child will be stacked behind it. This flag is useful for drop shadow effects and for decoration objects that follow the parent item's geometry without drawing on top of it. |
| QGraphicsItem::ItemUsesExtendedStyleOption | 0x200 | Item makes use of either exposedRect or matrix in QStyleOptionGraphicsItem. By default, the exposedRect is initialized to the item's boundingRect() and the matrix is untransformed. You can enable this flag for the style options to be set up with more fine-grained values. Note that QStyleOptionGraphicsItem::levelOfDetail is unaffected by this flag and always initialized to 1. Use QStyleOptionGraphicsItem::levelOfDetailFromTransform() if you need a higher value. |
| QGraphicsItem::ItemHasNoContents | 0x400 | Item does not paint anything (i.e., calling paint() on the item has no effect). You should set this flag on items that do not need to be painted to ensure that Graphics View avoids unnecessary painting preparations. |
| QGraphicsItem::ItemSendsGeometryChanges | 0x800 | Item enables itemChange() notifications for ItemPositionChange, ItemPositionHasChanged, ItemMatrixChange, ItemTransformChange, ItemTransformHasChanged, ItemRotationChange, ItemRotationHasChanged, ItemScaleChange, ItemScaleHasChanged, ItemTransformOriginPointChange, and ItemTransformOriginPointHasChanged. For performance reasons, these notifications are disabled by default. You must enable this flag to receive notifications for position and transform changes. |
| QGraphicsItem::ItemAcceptsInputMethod | 0x1000 | Item supports input methods typically used for Asian languages. |
| QGraphicsItem::ItemNegativeZStacksBehindParent | 0x2000 | Item automatically stacks behind the parent if the z-value is negative. This flag enables setZValue() to toggle ItemStacksBehindParent. |
| QGraphicsItem::ItemIsPanel | 0x4000 | Item is a panel. A panel provides activation and contained focus handling. Only one panel can be active at a time (see QGraphicsItem::isActive()). When no panel is active, QGraphicsScene activates all non-panel items. Window items (i.e., QGraphicsItem::isWindow() returns true) are panels. |
| QGraphicsItem::ItemSendsScenePositionChanges | 0x10000 | Item enables itemChange() notifications for ItemScenePositionHasChanged. For performance reasons these notifications are disabled by default. You must enable this flag to receive notifications for scene position changes. |
| QGraphicsItem::ItemContainsChildrenInShape | 0x80000 | This flag indicates that all of the item's direct or indirect children only draw within the item's shape. Unlike ItemClipsChildrenToShape, this restriction is not enforced. Set ItemContainsChildrenInShape when you manually assure that drawing is bound to the item's shape and want to avoid the cost associated with enforcing the clip. Setting this flag enables more efficient drawing and collision detection. The flag is disabled by default. If both this flag and ItemClipsChildrenToShape are set, the clip will be enforced. This is equivalent to just setting ItemClipsChildrenToShape. |
This enum specifies the behavior of a modal panel which is a panel that blocks input to other panels.
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
QGraphicsItem::NonModal | 0 | Panel is not modal and does not block input to other panels. This is the default value for panels. |
QGraphicsItem::PanelModal | 1 | Panel is modal to a single item hierarchy and blocks input to its parent pane, all grandparent panels, and all siblings of its parent and grandparent panels. |
QGraphicsItem::SceneModal | 2 | Window is modal to the entire scene and blocks input to all panels. |
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
|
explicit |
Constructs a QGraphicsItem with the given parent item. If the parent is a nullptr the graphic item can be added to a scene by calling QGraphicsScene::addItem(). The graphic item will then become a top level item.
- See also
- QGraphicsScene::addItem(), setParentItem()
|
virtual |
Destroys the QGraphicsItem and all its children. If this QGraphicsItem is currently associated with a scene, the item will be removed from the scene before it is deleted.
Method Documentation
| bool QGraphicsItem::acceptDrops | ( | ) | const |
Returns true if this QGraphicsItem can accept drag and drop events, otherwise returns false. By default items do not accept drag and drop events.
- See also
- setAcceptDrops()
| Qt::MouseButtons QGraphicsItem::acceptedMouseButtons | ( | ) | const |
Returns the mouse buttons this QGraphicsItem can accept mouse events for. By default all mouse buttons are accepted. Mouse events are delivered to the first or top item in the Z order which accepts the mouse button.
| bool QGraphicsItem::acceptHoverEvents | ( | ) | const |
Returns true if an item accepts hover events (QGraphicsSceneHoverEvent), otherwise returns false. By default items do not accept hover events.
| bool QGraphicsItem::acceptTouchEvents | ( | ) | const |
Returns true if an item accepts touch events, otherwise returns false. By default items do not accept touch events.
- See also
- setAcceptTouchEvents()
|
virtual |
This method is called twice for all items by the QGraphicsScene::advance() slot. In the first phase all items are called with phase equal to 0, indicating that items on the scene are about to advance. Then all items are called with phase equal to 1.
Reimplement this method to update your item if you need simple scene-controlled animation. The default implementation does nothing.
For individual item animation, an alternative to this method is to either use QGraphicsItemAnimation, or to multiple-inherit from QObject and QGraphicsItem, and animate your item using QObject::startTimer() and QObject::timerEvent().
- See also
- QGraphicsItemAnimation, QTimeLine
|
pure virtual |
This method defines the outer bounds of the item as a rectangle. All painting must occur within the item's bounding rectangle. QGraphicsView uses this to determine when the item requires redrawing. Although the item's shape can be arbitrary, the bounding area is always a rectangle, and it is unaffected by the item's transformation.
Before changing the item's bounding rectangle, you must first call prepareGeometryChange(). This notifies the scene of the pending change, so the geometry index can be updated.
For shapes with an outline it is important to include half the pen width in the bounding rectangle. It is not necessary to compensate for antialiasing.
- See also
- boundingRegion(), shape(), contains(), The Graphics View Coordinate System, prepareGeometryChange()
Implemented in QGraphicsItemGroup::boundingRect(), QGraphicsSimpleTextItem::boundingRect(), QGraphicsTextItem::boundingRect(), QGraphicsPixmapItem::boundingRect(), QGraphicsLineItem::boundingRect(), QGraphicsPolygonItem::boundingRect(), QGraphicsEllipseItem::boundingRect(), QGraphicsRectItem::boundingRect(), QGraphicsPathItem::boundingRect(), QGraphicsSvgItem::boundingRect()
| QRegion QGraphicsItem::boundingRegion | ( | const QTransform & | itemToDeviceTransform | ) | const |
Returns the bounding region for this item. The value for itemToDeviceTransform is the transformation from item coordinates to device coordinates. If you pass an identity QTransform as a parameter this method will return a local coordinate region.
If you want this method to return a QRegion in scene coordinates, pass the return value of sceneTransform() as the itemToDeviceTransform argument.
The bounding region describes a coarse outline of the item's visual contents. The bounding region is more complex and more expensive to use than the bounding rectangle however the bounding region is more precise.
You can tune the granularity for the bounding region by first calling setBoundingRegionGranularity(). The default granularity is 0 which means the item's bounding region is the same as its bounding rectangle.
- See also
- boundingRegionGranularity()
| qreal QGraphicsItem::boundingRegionGranularity | ( | ) | const |
Returns the item's bounding region granularity which is a value between 0 and 1. The default value is 0 which is the lowest granularity and means the bounding region corresponds to the item's bounding rectangle.
- See also
- setBoundingRegionGranularity()
| CacheMode QGraphicsItem::cacheMode | ( | ) | const |
Returns the cache mode for this item. The default mode is NoCache which means the cache is disabled and all painting is immediate.
- See also
- setCacheMode()
| QList< QGraphicsItem * > QGraphicsItem::childItems | ( | ) | const |
Returns a list of this item's children. The items are sorted by stacking order. This takes into account both the item's insertion order and their Z values.
- See also
- setParentItem(), zValue(), Sorting
| QRectF QGraphicsItem::childrenBoundingRect | ( | ) | const |
Returns the bounding rectangle of this item's descendants in local coordinates. If the item has no children, this method returns an empty QRectF.
This return value does not include the bounding rectangle for the current item, only its children. If you need to include the current item's bounding rectangle then add boundingRect() to childrenBoundingRect() using QRectF::operator|().
This method is linear in complexity, it determines the size of the returned bounding rectangle by iterating through all descendants.
- See also
- boundingRect(), sceneBoundingRect()
| void QGraphicsItem::clearFocus | ( | ) |
Removes keyboard input focus from the current item. If the item had focus then a focus out event will be sent. Only items that set the QGraphicsItem::ItemIsFocusable flag or widgets that set an appropriate focus policy, can accept keyboard focus.
- See also
- setFocus(), hasFocus(), QGraphicsWidget::focusPolicy
| QPainterPath QGraphicsItem::clipPath | ( | ) | const |
Returns the clip path for this item or an empty QPainterPath if this item is not clipped. The clip path constrains the item's appearance and interaction. The item can not draw outside the clip path and events outside the clip path will not be delivered to the item.
Enable clipping by setting the ItemClipsToShape or ItemClipsChildrenToShape flags. The item's clip path is calculated by intersecting all clipping ancestors' shapes. If the item sets ItemClipsToShape, the final clip is intersected with the item's own shape.
Clipping introduces a performance penalty. Avoid using clipping whenever possible.
- See also
- isClipped(), shape(), setFlags()
|
virtual |
Returns true if this item collides with graphicsItem, otherwise returns false. The mode is applied to graphicsItem and the resulting shape or bounding rectangle is then compared to this item's shape. The default value for mode is Qt::IntersectsItemShape which means a collision occurs when the shape of graphicsItem intersects, contains, or is contained by this item's shape.
The default implementation is based on shape intersection. The process of shape intersection is expensive when the shapes are complex. You have the option of reimplementing this method in a subclass of QGraphicsItem to provide a custom algorithm. This allows you to make use of natural constraints in the shapes of your own items, in order to improve the performance of the collision detection. For instance, the collision of two untransformed perfectly circular items can be determined very efficiently by comparing their positions and radii.
When reimplementing this method and calling shape() or boundingRect() on the graphicsItem parameter, the returned coordinates must be mapped to this item's coordinate system before any intersection can take place.
- See also
- contains(), shape()
|
virtual |
Returns true if this item collides with path. The collision is determined by mode. The default value for mode is Qt::IntersectsItemShape which means the path collides with this item if it either intersects, contains, or is contained by this item's shape.
This method checks whether the item's shape or bounding rectangle (depending on mode) is contained within path and not whether path is contained within the items shape or bounding rectangle.
- See also
- collidesWithItem(), contains(), shape()
| QList< QGraphicsItem * > QGraphicsItem::collidingItems | ( | Qt::ItemSelectionMode | mode = Qt::IntersectsItemShape | ) | const |
Returns a list of all items in the current scene which collide with this QGraphicsItem. Every item shape or bounding rectangle is compared to the current QGraphicsItem.
Collisions are determined based on the given mode. The default value for mode is Qt::IntersectsItemShape.
- See also
- collidesWithItem()
| QGraphicsItem * QGraphicsItem::commonAncestorItem | ( | const QGraphicsItem * | graphicsItem | ) | const |
Returns the closest common parent of this QGraphicsItem and graphicsItem. If graphicsItem is a nullptr or there is no common parent, the return value is a nullptr.
- See also
- isAncestorOf()
|
virtual |
Returns true if this item contains point, which is in local coordinates, otherwise false is returned. It is most often called from QGraphicsView to determine what item is under the cursor, and for that reason, the implementation of this method should be as light-weight as possible.
By default this method calls shape(). You can override this method in a subclass to provide a implementation.
- See also
- shape(), boundingRect(), collidesWithPath()
Reimplemented in QGraphicsSimpleTextItem::contains(), QGraphicsTextItem::contains(), QGraphicsPixmapItem::contains(), QGraphicsLineItem::contains(), QGraphicsPolygonItem::contains(), QGraphicsEllipseItem::contains(), QGraphicsRectItem::contains(), QGraphicsPathItem::contains()
|
protectedvirtual |
The event handler for event can be reimplemented in a subclass to process context menu events. The event parameter contains details about the event to be handled. If you ignore the event, (i.e., by calling QEvent::ignore(),) event will propagate to any item beneath this item. If no items accept the event, it will be ignored by the scene, and propagate to the view.
The default implementation ignores the event.
It is common to open a QMenu in response to receiving a context menu event.
- See also
- sceneEvent()
Reimplemented in QGraphicsTextItem::contextMenuEvent()
| QCursor QGraphicsItem::cursor | ( | ) | const |
Returns the current cursor shape for this item.
| QVariant QGraphicsItem::data | ( | int | key | ) | const |
| QTransform QGraphicsItem::deviceTransform | ( | const QTransform & | viewportTransform | ) | const |
Returns this item's device transformation matrix using viewportTransform to map from scene to device coordinates. This matrix can be used to map coordinates and geometrical shapes from this item's local coordinate system to the viewport's (or any device's) coordinate system. To map coordinates from the viewport, you must first invert the returned matrix.
This method is the same as combining this item's scene transform with the view's viewport transform, but it also understands the ItemIgnoresTransformations flag. The device transform can be used to do accurate coordinate mapping (and collision detection) for untransformable items.
|
protectedvirtual |
The event handler for event can be reimplemented to receive drag enter events for this item. Drag enter events are generated as the cursor enters the item's area.
By accepting the event the item will accept drop events, in addition to receiving drag move and drag leave. Otherwise, the event will be ignored and propagate to the item beneath. If the event is accepted, the item will receive a drag move event before control goes back to the event loop.
Items do not receive drag and drop events by default, to enable this feature, call setAcceptDrops(true). The default implementation does nothing. A common implementation of dragEnterEvent accepts or ignores event depending on the associated mime data in event.
- See also
- dropEvent(), dragMoveEvent(), dragLeaveEvent()
Reimplemented in QGraphicsTextItem::dragEnterEvent()
|
protectedvirtual |
The event handler for event can be reimplemented to receive drag leave events for this item. Drag leave events are generated as the cursor leaves the item's area. Most often you will not need to reimplement this method, but it can be useful for resetting state in your item (e.g., highlighting).
Calling QEvent::ignore() or QEvent::accept() on event has no effect. Items do not receive drag and drop events by default, to enable this feature, call setAcceptDrops(true). The default implementation does nothing.
- See also
- dragEnterEvent(), dropEvent(), dragMoveEvent()
Reimplemented in QGraphicsTextItem::dragLeaveEvent()
|
protectedvirtual |
The event handler for event can be reimplemented to receive drag move events for this item. Drag move events are generated as the cursor moves around inside the item's area. Most often you will not need to reimplement this method; it is used to indicate that only parts of the item can accept drops.
Calling QEvent::ignore() or QEvent::accept() on event toggles whether or not the item will accept drops at the position from the event. By default event is accepted, indicating that the item allows drops at the specified position.
Items do not receive drag and drop events by default, to enable this feature, call setAcceptDrops(true). The default implementation does nothing.
- See also
- dropEvent(), dragEnterEvent(), dragLeaveEvent()
Reimplemented in QGraphicsTextItem::dragMoveEvent()
|
protectedvirtual |
The event handler for event can be reimplemented to receive drop events for this item. Items can only receive drop events if the last drag move event was accepted.
Calling QEvent::ignore() or QEvent::accept() on event has no effect. Items do not receive drag and drop events by default, to enable this feature, call setAcceptDrops(true). The default implementation does nothing.
- See also
- dragEnterEvent(), dragMoveEvent(), dragLeaveEvent()
Reimplemented in QGraphicsTextItem::dropEvent()
| qreal QGraphicsItem::effectiveOpacity | ( | ) | const |
Returns this item's effective opacity which is between 0.0 (transparent) and 1.0 (opaque). This value is a combination of this item's local opacity, and its parent and ancestors opacities. The effective opacity decides how the item is rendered.
- See also
- opacity(), paint(), setOpacity()
| void QGraphicsItem::ensureVisible | ( | const QRectF & | rectF = QRectF(), |
| int | xmargin = 50, |
||
| int | ymargin = 50 |
||
| ) |
If the current item is part of a scene that is viewed by a QGraphicsView, this method will attempt to scroll the view to ensure that rectF is visible inside the view's viewport. If rectF is a null rectangle (the default), QGraphicsItem will default to the item's bounding rectangle. The values for xmargin and ymargin are the number of pixels the view should use for margins.
If the QGraphicsView is unable to scroll to the specified rectF the contents are scrolled to the nearest valid position. If this item is not viewed by a QGraphicsView, this method does nothing.
- See also
- QGraphicsView::ensureVisible()
|
inline |
Equivalent to calling ensureVisible(QRectF(x, y, width, height), xmargin, ymargin).
| bool QGraphicsItem::filtersChildEvents | ( | ) | const |
Returns true if this item filters child events, otherwise false is returned. The default value is false and child events are not filtered.
- See also
- setFiltersChildEvents()
| GraphicsItemFlags QGraphicsItem::flags | ( | ) | const |
Returns the flags for this item. The flags describe what configurable features of the item are enabled and not. For example, if the flags include QGraphicsItem::ItemIsFocusable, the item can accept input focus. By default no flags are enabled.
- See also
- setFlags(), setFlag()
|
protectedvirtual |
The event handler for event can be reimplemented to receive focus in events for this item. The default implementation calls ensureVisible().
- See also
- focusOutEvent(), sceneEvent(), setFocus()
Reimplemented in QGraphicsTextItem::focusInEvent()
| QGraphicsItem * QGraphicsItem::focusItem | ( | ) | const |
If this item or any of its children currently has input focus, this method will return a pointer to that item. If no descendant has input focus then a nullptr is returned.
- See also
- hasFocus(), setFocus(), QWidget::focusWidget()
|
protectedvirtual |
The event handler for event can be reimplemented to receive focus out events for this item. The default implementation does nothing.
- See also
- focusInEvent(), sceneEvent(), setFocus()
Reimplemented in QGraphicsTextItem::focusOutEvent()
| QGraphicsItem * QGraphicsItem::focusProxy | ( | ) | const |
Returns this item's focus proxy or nullptr if this item has no focus proxy.
- See also
- setFocusProxy(), setFocus(), hasFocus()
| void QGraphicsItem::grabKeyboard | ( | ) |
Grabs the keyboard input. The item will receive all keyboard input to the scene until one of the following events occurs:
- Item becomes invisible
- Item is removed from the scene
- Item is deleted
- Item calls ungrabKeyboard()
- Another item calls grabKeyboard(), then this item will regain the keyboard grab when the other item calls ungrabKeyboard()
When an item gains the keyboard grab, it receives a QEvent::GrabKeyboard event. When it loses the keyboard grab, it receives a QEvent::UngrabKeyboard event. These events can be used to detect when an item gains or loses the keyboard grab through other means than gaining input focus.
It is almost never necessary to explicitly grab the keyboard input since "grabs and releases" are done automatically as items gain and lose focus. Only visible items can grab keyboard input. Calling grabKeyboard() on an invisible item has no effect.
- See also
- ungrabKeyboard(), grabMouse(), setFocus()
| void QGraphicsItem::grabMouse | ( | ) |
Grabs the mouse input. This item will receive all mouse events for the scene until any of the following events occurs:
- Item becomes invisible
- Item is removed from the scene/li>
- Item is deleted
- Item calls ungrabMouse()
- Another item calls grabMouse(), then this item will regain the mouse grab when the other item calls ungrabMouse()
When an item gains the mouse grab, it receives a QEvent::GrabMouse event. When it loses the mouse grab, it receives a QEvent::UngrabMouse event. These events can be used to detect when an item gains or loses the mouse grab through other means than receiving mouse button events.
It is almost never necessary to explicitly grab the mouse since "grabs and releases" are done automatically as mouse buttons are pressed and released. Only visible items can grab mouse input. Calling grabMouse() on an invisible item has no effect.
| QGraphicsEffect * QGraphicsItem::graphicsEffect | ( | ) | const |
Returns a pointer to this item's effect if it has one, otherwise returns a nullptr.
- See also
- setGraphicsEffect()
| QGraphicsItemGroup * QGraphicsItem::group | ( | ) | const |
Returns a pointer to this item's item group or a nullptr if this item is not member of a group.
|
deprecated |
- Deprecated:
- Returns true if this item handles child events (i.e., all events intended for any of its children are instead sent to this item), otherwise false is returned.
This property is useful for item groups; it allows one item to handle events on behalf of its children, as opposed to its children handling their events individually.
The default is to return false; children handle their own events. The exception for this is if the item is a QGraphicsItemGroup, then it defaults to return true.
| bool QGraphicsItem::hasCursor | ( | ) | const |
Returns true if this item has a cursor set, otherwise false is returned.
By default, items do not have any cursor set. cursor() will return a standard pointing arrow cursor.
- See also
- unsetCursor()
| bool QGraphicsItem::hasFocus | ( | ) | const |
Returns true if this item is active and it or its focus proxy has keyboard input focus, otherwise returns false.
|
inline |
This method is equivalent to calling setVisible(false).
- See also
- show(), setVisible()
|
protectedvirtual |
The event handler for event can be reimplemented to receive hover enter events for this item. The default implementation calls update(). Calling QEvent::ignore() or QEvent::accept() on event has no effect.
Reimplemented in QGraphicsTextItem::hoverEnterEvent()
|
protectedvirtual |
The event handler for event can be reimplemented to receive hover leave events for this item. The default implementation calls update(). Calling QEvent::ignore() or QEvent::accept() on event has no effect.
Reimplemented in QGraphicsTextItem::hoverLeaveEvent()
|
protectedvirtual |
The event handler for event can be reimplemented to receive hover move events for this item. The default implementation does nothing. Calling QEvent::ignore() or QEvent::accept() on event has no effect.
Reimplemented in QGraphicsTextItem::hoverMoveEvent()
|
protectedvirtual |
The event handler for event can be reimplemented to receive input method events for this item. The default implementation ignores the event.
- See also
- inputMethodQuery(), sceneEvent()
Reimplemented in QGraphicsTextItem::inputMethodEvent()
| Qt::InputMethodHints QGraphicsItem::inputMethodHints | ( | ) | const |
Returns the current input method hints of this item.
Input method hints are only relevant for input items. The hints are used by the input method to indicate how it should operate. For example, if the Qt::ImhNumbersOnly flag is set, the input method may change its visual components to reflect that only numbers can be entered.
The effect may vary between input method implementations.
- See also
- setInputMethodHints(), inputMethodQuery()
|
protectedvirtual |
This method is only relevant for input items. It is used by the input method to query a set of properties of the item to be able to support complex input method operations, such as support for surrounding text and reconversions. The query parameter specifies which property is queried.
- See also
- inputMethodEvent(), QInputMethodEvent
Reimplemented in QGraphicsTextItem::inputMethodQuery()
| void QGraphicsItem::installSceneEventFilter | ( | QGraphicsItem * | filterItem | ) |
Installs an event filter for this item on filterItem, causing all events for this item to first pass through filterItem's sceneEventFilter() method. An item can only filter events for other items in the same scene. Also, an item can not filter its own events; instead, you can reimplement sceneEvent() directly. Items must belong to a scene for scene event filters to be installed and used.
To filter another item's events, install this QGraphicsItem as the event filter for the other item.
| bool QGraphicsItem::isActive | ( | ) | const |
Returns true if this item is active, otherwise returns false. An item can only be active if the scene is active. An item is active if it is, or is a descendant of, an active panel. Items in non-active panels are not active. Items that are not part of a panel follow scene activation when the scene has no active panel. Only active items can gain input focus.
| bool QGraphicsItem::isAncestorOf | ( | const QGraphicsItem * | graphicsItem | ) | const |
Returns true if this item is the parent of graphicsItem.
- See also
- parentItem()
| bool QGraphicsItem::isBlockedByModalPanel | ( | QGraphicsItem ** | blockingPanel = nullptr | ) | const |
Returns true if this item is blocked by a modal panel, false otherwise. If blockingPanel is not a nullptr it will be set to the modal panel that is blocking this item. If this item is not blocked, blockingPanel will not be set by this method. This method always returns false for items not in a scene.
- See also
- panelModality(), setPanelModality(), PanelModality
| bool QGraphicsItem::isClipped | ( | ) | const |
Returns true if this item is clipped. An item is clipped if it has either set the ItemClipsToShape flag, or if it or any of its ancestors has set the ItemClipsChildrenToShape flag.
Clipping affects the item's appearance as well as mouse and hover event delivery.
- See also
- clipPath(), shape(), setFlags()
| bool QGraphicsItem::isEnabled | ( | ) | const |
Returns true if the item is enabled, otherwise false is returned.
- See also
- setEnabled()
Returns true if rectF is completely obscured by other items.
- See also
- opaqueArea()
This method is equivalent to calling isObscured(QRectF(x, y, width, height)).
|
virtual |
Returns true if the current QGraphicsItem's bounding rectangle is completely obscured by graphicsItem.
The base implementation maps the graphicsItem opaqueArea() to the current QGraphicsItem's coordinate system and then checks if the current boundingRect() is fully contained within the mapped shape. You can reimplement this method to provide a custom algorithm for determining whether the current item is obscured by graphicsItem.
- See also
- opaqueArea(), isObscured()
Reimplemented in QGraphicsItemGroup::isObscuredBy(), QGraphicsSimpleTextItem::isObscuredBy(), QGraphicsTextItem::isObscuredBy(), QGraphicsPixmapItem::isObscuredBy(), QGraphicsLineItem::isObscuredBy(), QGraphicsPolygonItem::isObscuredBy(), QGraphicsEllipseItem::isObscuredBy(), QGraphicsRectItem::isObscuredBy(), QGraphicsPathItem::isObscuredBy(), QAbstractGraphicsShapeItem::isObscuredBy()
| bool QGraphicsItem::isPanel | ( | ) | const |
Returns true if the item is a panel, otherwise returns false.
- See also
- panel(), GraphicsItemFlag::ItemIsPanel
| bool QGraphicsItem::isSelected | ( | ) | const |
Returns true if this item is selected, otherwise false is returned. Items that are in a group inherit the group's selected state. Items are not selected by default.
| bool QGraphicsItem::isUnderMouse | ( | ) | const |
Returns true if this item is currently under the mouse cursor in one of the views, otherwise false is returned.
- See also
- QGraphicsScene::views(), QCursor::pos()
| bool QGraphicsItem::isVisible | ( | ) | const |
Returns true if the item is visible, otherwise, false is returned. The item's general visibility is unrelated to whether or not it is actually being visualized by a QGraphicsView.
- See also
- setVisible()
| bool QGraphicsItem::isVisibleTo | ( | const QGraphicsItem * | graphicsItem | ) | const |
Returns true if the item is visible to graphicsItem, otherwise false is returned. The graphicsItem can be a nullptr in which case this method will return whether the item is visible to the scene or not.
An item may not be visible to its ancestors even if isVisible() is true. It may also be visible to its ancestors even if isVisible() is false. If any ancestor is hidden, the item itself will be implicitly hidden, in which case this method will return false.
- See also
- isVisible(), setVisible()
| bool QGraphicsItem::isWidget | ( | ) | const |
Returns true if this item inherits from QGraphicsWidget, otherwise returns false.
| bool QGraphicsItem::isWindow | ( | ) | const |
Returns true if the item is a QGraphicsWidget window, otherwise returns false.
- See also
- QGraphicsWidget::windowFlags()
|
protectedvirtual |
This method is called by QGraphicsItem to notify custom items, the state of the current item is being modified. By overriding this method in your class, custom items can react to the change. The parameter for value will be the new value of the property which is changing.
The default implementation does nothing and returns value. Certain QGraphicsItem methods can not be called when overriding this method. Refer to GraphicsItemChange for additional information.
| QTransform QGraphicsItem::itemTransform | ( | const QGraphicsItem * | graphicsItem, |
| bool * | ok = nullptr |
||
| ) | const |
Returns a QTransform that maps coordinates from this item to graphicsItem. If ok is not null, and if there is no such transform, the boolean pointed to by ok will be set to false, otherwise it will be set to true.
This transform provides an alternative to the mapToItem() or mapFromItem() methods, by returning the appropriate transform so that you can map shapes and coordinates yourself. It also helps you write more efficient code when repeatedly mapping between the same two items.
- Note
- In rare circumstances there is no transform that maps between two items.
- See also
- mapToItem(), mapFromItem(), deviceTransform()
|
protectedvirtual |
The event handler for event can be reimplemented to receive key press events for this item. The default implementation ignores the event. Key events are only received for items that set the QGraphicsItem::ItemIsFocusable flag and that have keyboard input focus.
Reimplemented in QGraphicsTextItem::keyPressEvent()
|
protectedvirtual |
The event handler for event can be reimplemented to receive key release events for this item. The default implementation ignores the event. Key events are only received for items that set the QGraphicsItem::ItemIsFocusable flag and that have keyboard input focus.
Reimplemented in QGraphicsTextItem::keyReleaseEvent()
| QPainterPath QGraphicsItem::mapFromItem | ( | const QGraphicsItem * | graphicsItem, |
| const QPainterPath & | path | ||
| ) | const |
Maps the path which is in the graphicsItem coordinate system, to the current QGraphicsItem coordinate system. Returns the mapped path. If graphicsItem is a nullptr this method returns the same as mapFromScene().
| QPointF QGraphicsItem::mapFromItem | ( | const QGraphicsItem * | graphicsItem, |
| const QPointF & | point | ||
| ) | const |
Maps the point which is in the graphicsItem coordinate system, to the current QGraphicsItem coordinate system. Returns the mapped coordinate. If graphicsItem is a nullptr this method returns the same as mapFromScene().
| QPolygonF QGraphicsItem::mapFromItem | ( | const QGraphicsItem * | graphicsItem, |
| const QPolygonF & | polygon | ||
| ) | const |
Maps the polygon which is in the graphicsItem coordinate system, to the current QGraphicsItem coordinate system. Returns the mapped polygon. If graphicsItem is a nullptr this method returns the same as mapFromScene().
| QPolygonF QGraphicsItem::mapFromItem | ( | const QGraphicsItem * | graphicsItem, |
| const QRectF & | rectF | ||
| ) | const |
Maps the rectF which is in the graphicsItem coordinate system, to the current QGraphicsItem coordinate system. Returns the mapped rectangle as a polygon. If graphicsItem is a nullptr this method returns the same as mapFromScene().
|
inline |
This method is equivalent to calling mapFromItem(graphicsItem, QPointF(x, y)).
|
inline |
This method is equivalent to calling mapFromItem(graphicsItem, QRectF(x, y, width, height)).
| QPainterPath QGraphicsItem::mapFromParent | ( | const QPainterPath & | path | ) | const |
Maps the path which is in the parent's coordinate system, to the current QGraphicsItem coordinate system, and returns the mapped path.
Maps the point which is in the parent's coordinate system, to the current QGraphicsItem coordinate system, and returns the mapped coordinate.
Maps the polygon which is in the parent's coordinate system, to the current QGraphicsItem coordinate system, and returns the mapped polygon.
Maps the rectf which is in the parent's coordinate system, to the current QGraphicsItem coordinate system, and returns the mapped rectangle as a polygon.
This method is equivalent to calling mapFromParent(QPointF(x, y)).
This method is equivalent to calling mapFromItem(QRectF(x, y, width, height)).
| QPainterPath QGraphicsItem::mapFromScene | ( | const QPainterPath & | path | ) | const |
Maps the path which is in the scene's coordinate system, to the current QGraphicsItem coordinate system, and returns the mapped path.
Maps the point which is in the scene's coordinate system, to the current QGraphicsItem coordinate system, and returns the mapped coordinate.
Maps the polygon which is in the scene's coordinate system, to the current QGraphicsItem coordinate system, and returns the mapped polygon.
Maps the rectF which is in the scene's coordinate system, to the current QGraphicsItem coordinate system, and returns the mapped rectangle as a polygon.
This method is equivalent to calling mapFromScene(QPointF(x, y)).
This method is equivalent to calling mapFromScene(QRectF(x, y, width, height)).
| QRectF QGraphicsItem::mapRectFromItem | ( | const QGraphicsItem * | graphicsItem, |
| const QRectF & | rectF | ||
| ) | const |
Maps the rectF which is in the graphicsItem coordinate system, to the current QGraphicsItem coordinate system, and returns the mapped rectangle as a new rectangle.
If graphicsItem is a nullptr this method returns the same as mapRectFromScene().
|
inline |
This method is equivalent to calling mapRectFromItem(graphicsItem, QRectF(x, y, width, height)).
Maps the rectF which is in the parent's coordinate system, to the current QGraphicsItem coordinate system, and returns the mapped rectangle as a new rectangle.
|
inline |
This method is equivalent to calling mapRectFromParent(QRectF(x, y, width, height)).
Maps the rectF which is in the scene's coordinate system, to the current QGraphicsItem coordinate system, and returns the mapped rectangle as a new rectangle.
This method is equivalent to calling mapRectFromScene(QRectF(x, y, width, height)).
| QRectF QGraphicsItem::mapRectToItem | ( | const QGraphicsItem * | graphicsItem, |
| const QRectF & | rectF | ||
| ) | const |
Maps the rectF which is in the current QGraphicsItem coordinate system, to the graphicsItem coordinate system. Returns the mapped rectangle as a new rectangle. If graphicsItem is a nullptr this method returns the same as mapRectToScene().
|
inline |
This method is equivalent to calling mapRectToItem(graphicsItem, QRectF(x, y, width, height)).
Maps the rectF, which is in the current QGraphicsItem coordinate system, to the parent's coordinate system. Returns the mapped rectangle as a new rectangle.
This method is equivalent to calling mapRectToParent(QRectF(x, y, width, height)).
Maps the rectF, which is in the current QGraphicsItem coordinate system, to the scene's coordinate system. Returns the mapped rectangle as a new rectangle.
This method is equivalent to calling mapRectToScene(QRectF(x, y, width, height)).
| QPainterPath QGraphicsItem::mapToItem | ( | const QGraphicsItem * | graphicsItem, |
| const QPainterPath & | path | ||
| ) | const |
Maps the path which is in the current QGraphicsItem coordinate system, to the graphicsItem coordinate system. Returns the mapped path. If graphicsItem is a nullptr this method returns the same as mapToScene().
| QPointF QGraphicsItem::mapToItem | ( | const QGraphicsItem * | graphicsItem, |
| const QPointF & | point | ||
| ) | const |
Maps the point which is in the current QGraphicsItem coordinate system, to the graphicsItem coordinate system. Returns the mapped coordinate. If graphicsItem is a nullptr this method returns the same as mapToScene().
| QPolygonF QGraphicsItem::mapToItem | ( | const QGraphicsItem * | graphicsItem, |
| const QPolygonF & | polygon | ||
| ) | const |
Maps the polygon which is in the current QGraphicsItem coordinate system, to the graphicsItem coordinate system. Returns the mapped polygon. If graphicsItem is a nullptr this method returns the same as mapToScene().
| QPolygonF QGraphicsItem::mapToItem | ( | const QGraphicsItem * | graphicsItem, |
| const QRectF & | rectF | ||
| ) | const |
Maps the rectF which is in the current QGraphicsItem coordinate system, to the graphicsItem coordinate system. Returns the mapped rectangle as a polygon. If graphicsItem is a nullptr this method returns the same as mapToScene().
| QPainterPath QGraphicsItem::mapToParent | ( | const QPainterPath & | path | ) | const |
Maps the path which is in the current QGraphicsItem coordinate system, to the parent's coordinate system. Returns the mapped path. If the current QGraphicsItem has no parent, then path will be mapped to the scene's coordinate system.
Maps the point which is in the current QGraphicsItem coordinate system, to the parent's coordinate system. Returns the mapped coordinate. If the current QGraphicsItem has no parent then point will be mapped to the scene's coordinate system.
Maps the polygon which is in the current QGraphicsItem coordinate system, to the parent's coordinate system. Returns the mapped polygon. If the current QGraphicsItem has no parent then polygon will be mapped to the scene's coordinate system.
Maps the rectF which is in the current QGraphicsItem coordinate system, to the parent's coordinate system. Returns the mapped rectangle as a polygon. If the current QGraphicsItem has no parent then rectF will be mapped to the scene's coordinate system.
This method is equivalent to calling mapToParent(QPointF(x, y)).
This method is equivalent to calling mapToParent(QRectF(x, y, width, height)).
| QPainterPath QGraphicsItem::mapToScene | ( | const QPainterPath & | path | ) | const |
Maps the path which is in the current QGraphicsItem coordinate system, to the scene's coordinate system. Returns the mapped path.
Maps the point which is in the current QGraphicsItem coordinate system, to the scene's coordinate system. Returns the mapped coordinate.
Maps the polygon which is in the current QGraphicsItem coordinate system, to the scene's coordinate system. Returns the mapped polygon.
Maps the rectF which is in the current QGraphicsItem coordinate system, to the scene's coordinate system. Returns the mapped rectangle as a polygon.
This method is equivalent to calling mapToScene(QPointF(x, y)).
This method is equivalent to calling mapToScene(QRectF(x, y, width, height)).
|
deprecated |
- Deprecated:
- Returns the item's affine transformation matrix. This is a subset or the item's full transformation matrix, and might not represent the item's full transformation.
Use transform() instead.
|
protectedvirtual |
The event handler for event can be reimplemented to receive mouse doubleclick events for this item. When doubleclicking the item will first receive a mouse press event, followed by a release event, then a doubleclick event, and finally a release event. An item will not receive double click events if it is neither selectable nor movable.
Calling QEvent::ignore() or QEvent::accept() on the event has no effect.
The default implementation calls mousePressEvent(). If you want to keep the base implementation when reimplementing this method, call QGraphicsItem::mouseDoubleClickEvent() in your reimplementation.
Reimplemented in QGraphicsTextItem::mouseDoubleClickEvent()
|
protectedvirtual |
The event handler for event can be reimplemented to receive mouse move events for this item. If you do receive this event, you can be certain that this item also received a mouse press event, and that this item is the current mouse grabber. The mousePressEvent() method decides which graphics item should receive mouse events.
Calling QEvent::ignore() or QEvent::accept() on the event has no effect.
The default implementation handles basic item interaction, such as selection and moving. If you want to keep the base implementation when reimplementing this method, call QGraphicsItem::mouseMoveEvent() in your reimplementation.
Reimplemented in QGraphicsTextItem::mouseMoveEvent()
|
protectedvirtual |
The event handler for event can be reimplemented to receive mouse press events for this item. Mouse press events are only delivered to items which accept the mouse button which was pressed. By default, an item accepts all mouse buttons however this can be changed by calling setAcceptedMouseButtons(). The mouse press event decides which item should become the mouse grabber.
If you do not reimplement this method the mouse press event will propagate to other items below this item. If you do reimplement this method, the event will be accepted and this item will grab the mouse input. Grabbing the mouse input allows the item to receive future move, release, and doubleclick events.
If you call QEvent::ignore() on event, this item will lose the mouse grab and event will propagate to any topmost item beneath. No further mouse events will be delivered to this item unless a new mouse press event is received.
The default implementation handles basic item interactions, such as selection and moving. If you want to keep the base implementation when reimplementing this method, call QGraphicsItem::mousePressEvent() in your reimplementation. The default implementation calls QEvent::ignore() for items which are neither movable nor selectable.
Reimplemented in QGraphicsTextItem::mousePressEvent()
|
protectedvirtual |
The event handler for event can be reimplemented to receive mouse release events for this item. Calling QEvent::ignore() or QEvent::accept() on the event has no effect.
The default implementation handles basic item interaction, such as selection and moving. If you want to keep the base implementation when reimplementing this method, call QGraphicsItem::mouseReleaseEvent() in your reimplementation.
Reimplemented in QGraphicsTextItem::mouseReleaseEvent()
This method is equivalent to calling setPos(pos() + QPointF(dx, dy)).
| qreal QGraphicsItem::opacity | ( | ) | const |
Returns the current QGraphicsItem local opacity which is between 0.0 (transparent) and 1.0 (opaque). This value is combined with any parent values into the effectiveOpacity(). The default opacity is 1.0 and fully opaque.
The effective opacity decides how the item is rendered. The opacity property decides the state of the painter passed to the paint() method. If the item is cached by using ItemCoordinateCache or DeviceCoordinateCache, the effective property will be applied to the item's cache as it is rendered.
|
virtual |
Returns a shape representing the area where this item is opaque. An area is opaque if it is filled using an opaque brush or color (i.e., not transparent). This method is used by isObscuredBy(), which is called by underlying items to determine if they are obscured by this item.
The default implementation returns an empty QPainterPath, indicating that this item is completely transparent and does not obscure any other items.
- See also
- isObscuredBy(), isObscured(), shape()
Reimplemented in QGraphicsItemGroup::opaqueArea(), QGraphicsSimpleTextItem::opaqueArea(), QGraphicsTextItem::opaqueArea(), QGraphicsPixmapItem::opaqueArea(), QGraphicsLineItem::opaqueArea(), QGraphicsPolygonItem::opaqueArea(), QGraphicsEllipseItem::opaqueArea(), QGraphicsRectItem::opaqueArea(), QGraphicsPathItem::opaqueArea(), QAbstractGraphicsShapeItem::opaqueArea()
|
pure virtual |
This method is usually called by QGraphicsView and paints the contents of an item in local coordinates.
Reimplement this method in a QGraphicsItem subclass to provide the item's painting implementation, using painter. The option parameter provides style options for the item, such as its state, exposed area and its level-of-detail hints. If widget is provided, it points to the widget that is being painted on, otherwise it is a nullptr. For cached painting widget is always a nullptr.
The painter's pen is 0-width by default, and its pen is initialized to the QPalette::Text brush from the paint device's palette. The brush is initialized to QPalette::Window.
Make sure to constrain all painting inside the boundaries of boundingRect() to avoid rendering artifacts (as QGraphicsView does not clip the painter for you). When QPainter renders the outline of a shape using an assigned QPen, half of the outline will be drawn outside the shape you are rendering. QGraphicsItem does not support use of cosmetic pens with a non-zero width. All painting is done in local coordinates.
Implemented in QGraphicsItemGroup::paint(), QGraphicsLineItem::paint(), QGraphicsPolygonItem::paint(), QGraphicsEllipseItem::paint(), QGraphicsRectItem::paint(), QGraphicsPathItem::paint(), QGraphicsSvgItem::paint(), QGraphicsSimpleTextItem::paint(), QGraphicsTextItem::paint(), QGraphicsPixmapItem::paint()
| QGraphicsItem * QGraphicsItem::panel | ( | ) | const |
Returns the QGraphicsItem panel or a nullptr if this item does not have a panel. If the item is a panel, it will return itself. Otherwise it will return the closest ancestor that is a panel.
- See also
- isPanel(), GraphicsItemFlag::ItemIsPanel
| PanelModality QGraphicsItem::panelModality | ( | ) | const |
Returns the modality for this item.
- See also
- setPanelModality()
| QGraphicsItem * QGraphicsItem::parentItem | ( | ) | const |
Returns a pointer to the current QGraphicsItem parent. If this item does not have a parent then nullptr is returned.
- See also
- setParentItem(), childItems()
| QGraphicsObject * QGraphicsItem::parentObject | ( | ) | const |
Returns a pointer to the current QGraphicsItem parent, cast to a QGraphicsObject. Returns a nullptr if the parent item is not a QGraphicsObject.
- See also
- parentItem(), childItems()
| QGraphicsWidget * QGraphicsItem::parentWidget | ( | ) | const |
Returns a pointer to the current QGraphicsItem parent widget. The item's parent widget is the closest parent item that is a widget.
- See also
- parentItem(), childItems()
| QPointF QGraphicsItem::pos | ( | ) | const |
Returns the position of the current QGraphicsItem in parent coordinates. If the item has no parent the position is given in scene coordinates. The position of the item describes its origin (local coordinate (0, 0)) in parent coordinates. Equivalent to mapToParent(0, 0).
To determine the item's position in scene coordinates, regardless of its parent, call scenePos().
- See also
- x(), y(), setPos(), transform(), The Graphics View Coordinate System
|
protected |
Prepares the item for a geometry change. Call this method before changing the bounding rect of an item to keep QGraphicsScene's index up to date. This method will call update() if necessary.
- See also
- boundingRect()
| void QGraphicsItem::removeSceneEventFilter | ( | QGraphicsItem * | filterItem | ) |
Removes an event filter on this item from filterItem.
- See also
- installSceneEventFilter()
|
deprecated |
- Deprecated:
- Use resetTransform() instead.
| void QGraphicsItem::resetTransform | ( | ) |
Resets this item's transformation matrix to the identity matrix or all the transformation properties to their default values. This is equivalent to calling setTransform(QTransform()).
- See also
- setTransform(), transform()
| qreal QGraphicsItem::rotation | ( | ) | const |
Returns the clockwise rotation, in degrees, around the Z axis. The default value is 0 which means the item is not rotated. The rotation is combined with the item's scale(), transform() and transformations() to map the item's coordinate system to the parent item.
- See also
- setRotation(), transformOriginPoint()
| qreal QGraphicsItem::scale | ( | ) | const |
Returns the scale factor of the item. The default scale factor is 1.0 which means the item is not scaled. The scale is combined with the item's rotation(), transform() and transformations() to map the item's coordinate system to the parent item.
- See also
- setScale(), rotation()
| QGraphicsScene * QGraphicsItem::scene | ( | ) | const |
Returns the current scene for the item or a nullptr if the item is not stored in a scene.
To add or move an item to a scene, call QGraphicsScene::addItem().
| QRectF QGraphicsItem::sceneBoundingRect | ( | ) | const |
Returns the bounding rect of this item in scene coordinates, by combining sceneTransform() with boundingRect().
|
protectedvirtual |
This method receives events to this item. Reimplement this method to intercept events before they are dispatched to the specialized event handlers contextMenuEvent(), focusInEvent(), focusOutEvent(), hoverEnterEvent(), hoverMoveEvent(), hoverLeaveEvent(), keyPressEvent(), keyReleaseEvent(), mousePressEvent(), mouseReleaseEvent(), mouseMoveEvent(), and mouseDoubleClickEvent().
Returns true if the event was recognized and handled, otherwise false is returned. The event is the intercepted event.
Reimplemented in QGraphicsTextItem::sceneEvent()
|
protectedvirtual |
Filters events for the item watched. The event is the filtered event.
Reimplementing this method in a subclass makes it possible for the item to be used as an event filter for other items, intercepting all the events sent to those items before they are able to respond. Reimplementations must return true to prevent further processing of a given event, ensuring that it will not be delivered to the watched item, or return false to indicate that the event should be propagated further by the event system.
- See also
- installSceneEventFilter()
|
deprecated |
- Deprecated:
- Use sceneTransform() instead.
| QPointF QGraphicsItem::scenePos | ( | ) | const |
Returns the item's position in scene coordinates. This is equivalent to calling mapToScene(0, 0).
| QTransform QGraphicsItem::sceneTransform | ( | ) | const |
Returns this item's scene transformation matrix. This matrix can be used to map coordinates and geometrical shapes from this item's local coordinate system to the scene's coordinate system. To map coordinates from the scene, you must first invert the returned matrix.
Unlike transform() which returns only an item's local transformation, this method includes the item's and any parent's position, and all the transformation properties.
Scrolls the contents of rectF by dx, dy. If rectF is a null rectangle, the item's bounding rectangle is scrolled.
Scrolling provides a fast alternative to simply redrawing when the contents of the item (or parts of the item) are shifted vertically or horizontally. Depending on the current transformation and the capabilities of the paint device (i.e., the viewport), this operation may consist of simply moving pixels from one location to another using memmove(). In most cases this is faster than rerendering the entire area.
After scrolling, the item will issue an update for the newly exposed areas. Scrolling is only supported when QGraphicsItem::ItemCoordinateCache is enabled. If scrolling is not supported, this method is equivalent to calling update(rectF).
If the item is opaque and not overlapped by other items, you can map the rectF to viewport coordinates and scroll the viewport as shown below
- See also
- boundingRect()
| void QGraphicsItem::setAcceptDrops | ( | bool | on | ) |
If on is true this item will accept drag and drop events, otherwise it is transparent for drag and drop events. By default, items do not accept drag and drop events.
- See also
- acceptDrops()
| void QGraphicsItem::setAcceptedMouseButtons | ( | Qt::MouseButtons | buttons | ) |
Sets the mouse buttons that this item accepts mouse events for. By default, all mouse buttons are accepted. If an item accepts a mouse button, it will become the mouse grabber item when a mouse press event is delivered for that button. However, if the item does not accept the mouse button, QGraphicsScene will forward the mouse events to the first item beneath it that does.
To disable mouse events for an item call setAcceptedMouseButtons(0).
- See also
- acceptedMouseButtons(), mousePressEvent()
| void QGraphicsItem::setAcceptHoverEvents | ( | bool | enabled | ) |
If enabled is true, this item will accept hover events, otherwise it will ignore them. By default, items do not accept hover events. Hover events are delivered when there is no current mouse grabber item. They are sent when the mouse cursor enters an item, when it moves around inside the item, and when the cursor leaves an item. Hover events are commonly used to highlight an item when the mouse enters the item.
Parent items receive hover enter events before their children, and leave events after their children. The parent does not receive a hover leave event if the cursor enters a child. The parent stays "hovered" until the cursor leaves the current area, including any children's areas.
If a parent item handles child events, it will receive hover move, drag move, and drop events as the cursor passes through its children, but it does not receive hover enter and hover leave, nor drag enter and drag leave events on behalf of its children.
A QGraphicsWidget with window decorations will accept hover events regardless of the value of acceptHoverEvents().
| void QGraphicsItem::setAcceptTouchEvents | ( | bool | enabled | ) |
If enabled is true this item will accept touch events, otherwise it will ignore them. By default items do not accept touch events.
- See also
- acceptTouchEvents()
| void QGraphicsItem::setActive | ( | bool | active | ) |
If active is true and the scene is active, this item's panel will be activated. Otherwise, the panel is deactivated.
If the item is not part of an active scene, active will decide what happens to the panel when the scene becomes active or the item is added to the scene. If true, the item's panel will be activated when the item is either added to the scene or the scene is activated. Otherwise, the item will stay inactive independent of the scene's activated state.
| void QGraphicsItem::setBoundingRegionGranularity | ( | qreal | granularity | ) |
Sets the bounding region granularity to granularity which is a value between and including 0 and 1. The default value is 0 which is the lowest granularity and the bounding region corresponds to the item's bounding rectangle.
The value of granularity describes the ratio between device resolution and the resolution of the bounding region. For example, a value of 0.25 will provide a region where each chunk corresponds to 4x4 device units / pixels.
The granularity is used by boundingRegion() to calculate how fine the bounding region of the item should be. The highest achievable granularity is 1, where boundingRegion() will return the finest outline possible for the respective device. For example, when using a QGraphicsView viewport, this gives you a pixel-perfect bounding region.
- See also
- boundingRegionGranularity()
Sets the item's cache mode to mode. The optional cacheSize argument is used only by ItemCoordinateCache mode, and describes the resolution of the cache buffer. If cacheSize is (100, 100), QGraphicsItem will fit the item into 100x100 pixels in graphics memory, regardless of the logical size of the item itself. By default QGraphicsItem uses the size of boundingRect(). For all other cache modes than ItemCoordinateCache, cacheSize is ignored.
Caching can speed up rendering if your item spends a significant time redrawing itself. In some cases the cache can also slow down rendering, in particular when the item spends less time redrawing than QGraphicsItem spends redrawing from the cache. When enabled, the item's paint() method will be called only once for each call to update(); for any subsequent repaint requests, the Graphics View system will redraw from the cache. This approach works particularly well with QGLWidget, which stores all the cache as OpenGL textures.
QPixmapCache's cache limit may need to be changed to obtain optimal performance. For more information about the different cache modes, refer to CacheMode.
| void QGraphicsItem::setCursor | ( | const QCursor & | cursor | ) |
Sets the current cursor shape for the item to cursor. The mouse cursor will assume this shape when it is over the current item. Refer to Qt::CursorShape for a list of predefined cursor objects and for a range of useful shapes. If no cursor has been set the cursor of the next item in the Z order is used.
For example, an editor item might want to use an I-beam cursor as shown below.
| void QGraphicsItem::setData | ( | int | key, |
| const QVariant & | value | ||
| ) |
Sets this item's custom data for the key to value. Custom item data is useful for storing arbitrary properties for any item. CopperSpice does not use this feature for storing data, it is provided for user applications.
- See also
- data()
| void QGraphicsItem::setEnabled | ( | bool | enabled | ) |
If enabled is true the item is enabled, otherwise it is disabled. Items are enabled by default.
Disabled items are visible, but they do not receive any events, and can not take focus nor be selected. Mouse events are discarded; they are not propagated unless the item is also invisible, or if it does not accept mouse events (see acceptedMouseButtons()). A disabled item can not become the mouse grabber, and as a result of this, an item loses the grab if it becomes disabled when grabbing the mouse, just like it loses focus if it had focus when it was disabled.
Disabled items are traditionally drawn using grayed-out colors (see QPalette::Disabled).
If you disable a parent item, all its children will also be disabled. If you enable a parent item, all children will be enabled, unless they have been explicitly disabled. For example, if you call setEnabled(false) on a child, it will not be re-enabled if its parent is disabled, and then enabled again.
If you install an event filter, you can still intercept events before they are delivered to items. This mechanism disregards the item's enabled state.
- See also
- isEnabled()
| void QGraphicsItem::setFiltersChildEvents | ( | bool | enabled | ) |
If enabled is true, this item is set to filter all events for all its children, otherwise if enabled is false, this item will only handle its own events. The default value is false.
- See also
- filtersChildEvents()
| void QGraphicsItem::setFlag | ( | GraphicsItemFlag | flag, |
| bool | enabled = true |
||
| ) |
If enabled is true the item flag is enabled, otherwise, it is disabled.
- See also
- flags(), setFlags()
| void QGraphicsItem::setFlags | ( | GraphicsItemFlags | flags | ) |
Sets the item flags to flags. All flags in flags are enabled, all flags not in flags are disabled. If the item had focus and flags does not enable QGraphicsItem::ItemIsFocusable, the item loses focus as a result of calling this method. Similarly, if the item was selected, and flags does not enabled ItemIsSelectable, the item is automatically unselected.
By default no flags are enabled. QGraphicsWidget enables the ItemSendsGeometryChanges flag by default in order to track position changes.
| void QGraphicsItem::setFocus | ( | Qt::FocusReason | focusReason = Qt::OtherFocusReason | ) |
Gives keyboard input focus to this item. The focusReason argument will be passed into any focus event generated by this method, it is used to give an explanation of what caused the item to get focus. Only enabled items that set the QGraphicsItem::ItemIsFocusable flag can accept keyboard focus.
If this item is not visible, not active, or not associated with a scene, it will not gain immediate input focus. However, it will be registered as the preferred focus item for its subtree of items, should it later become visible.
As a result of calling this method, this item will receive a focus in event with focusReason. If another item already has focus, that item will first receive a focus out event indicating that it has lost input focus.
- See also
- clearFocus(), hasFocus(), focusItem(), focusProxy()
| void QGraphicsItem::setFocusProxy | ( | QGraphicsItem * | graphicsItem | ) |
Sets the item's focus proxy to graphicsItem. If an item has a focus proxy, the focus proxy will receive input focus when the item gains input focus. The item itself will still have focus, but only the focus proxy will receive the keyboard input.
A focus proxy can itself have a focus proxy, and so on. In such case, keyboard input will be handled by the outermost focus proxy. The focus proxy graphicsItem must belong to the same scene as the current QGraphicsItem.
- See also
- focusProxy(), setFocus(), hasFocus()
| void QGraphicsItem::setGraphicsEffect | ( | QGraphicsEffect * | effect | ) |
Sets effect as the item's effect. If there already is an effect installed on this item, QGraphicsItem will delete the existing effect before installing the new effect. If effect is the installed on a different item, setGraphicsEffect() will remove the effect from the item and install it on this item.
QGraphicsItem takes ownership of effect. This method will apply the effect on itself and all its children.
- See also
- graphicsEffect()
| void QGraphicsItem::setGroup | ( | QGraphicsItemGroup * | group | ) |
Adds the current QGraphicsItems to the group. If group is a nullptr this item is removed from any current group and added as a child of the previous group's parent.
- See also
- group(), QGraphicsScene::createItemGroup()
|
deprecated |
- Deprecated:
- If enabled is true, this item is set to handle all events for all its children (i.e., all events intended for any of its children are instead sent to this item), otherwise if enabled is false, this item will only handle its own events. The default value is false.
This property is useful for item groups; it allows one item to handle events on behalf of its children, as opposed to its children handling their events individually.
If a child item accepts hover events, its parent will receive hover move events as the cursor passes through the child, but it does not receive hover enter and hover leave events on behalf of its child.
| void QGraphicsItem::setInputMethodHints | ( | Qt::InputMethodHints | hints | ) |
Sets the current input method hints of this item to hints.
- See also
- inputMethodHints(), inputMethodQuery()
|
deprecated |
- Deprecated:
- Sets the item's affine transformation matrix. This is a subset or the item's full transformation matrix, and might not represent the item's full transformation.
Use setTransform() instead.
| void QGraphicsItem::setOpacity | ( | qreal | opacity | ) |
Sets this item's local opacity, between 0.0 (transparent) and 1.0 (opaque). The item's local opacity is combined with parent and ancestor opacities into the effectiveOpacity(). By default, opacity propagates from parent to child, so if a parent's opacity is 0.5 and the child is also 0.5, the child's effective opacity will be 0.25.
The opacity property decides the state of the painter passed to the paint() method. If the item is cached, i.e., ItemCoordinateCache or DeviceCoordinateCache, the effective property will be applied to the item's cache as it is rendered.
There are two item flags which affect how the item's opacity is combined with the parent.
- QGraphicsItem::ItemIgnoresParentOpacity
- QGraphicsItem::ItemDoesntPropagateOpacityToChildren
| void QGraphicsItem::setPanelModality | ( | PanelModality | panelModality | ) |
Sets the modality for this item to panelModality. Changing the modality of a visible item takes effect immediately.
- See also
- panelModality()
| void QGraphicsItem::setParentItem | ( | QGraphicsItem * | parent | ) |
Sets the current QGraphicsItem parent to parent. If this item already has a parent, it is first removed from the previous parent. If parent is a nullptr this item will become a top-level item. This implicitly adds this QGraphicsItem to the scene of the parent. You should not add the item to the scene yourself.
Calling this method on an item that is an ancestor of parent is undefined behavior.
- See also
- parentItem(), childItems()
| void QGraphicsItem::setPos | ( | const QPointF & | pos | ) |
Sets the position of the item to pos, which is in parent coordinates. For items with no parent pos is in scene coordinates. The position of the item describes its origin (local coordinate (0, 0)) in parent coordinates.
| void QGraphicsItem::setRotation | ( | qreal | angle | ) |
Sets the clockwise rotation angle, in degrees, around the Z axis. The default value is 0 which means the item is not rotated. Assigning a negative value will rotate the item counter-clockwise. Normally the rotation angle is in the range (-360, 360), but it is also possible to assign values outside of this range. For example, a rotation of 370 degrees is the same as a rotation of 10 degrees.
The item is rotated around its transform origin point, which by default is (0, 0). You can select a different transformation origin by calling setTransformOriginPoint(). The rotation is combined with the item's scale(), transform() and transformations() to map the item's coordinate system to the parent item.
- See also
- rotation(), setTransformOriginPoint()
| void QGraphicsItem::setScale | ( | qreal | factor | ) |
Sets the scale factor of the current QGraphicsItem. The default scale factor is 1.0 which means the item is not scaled. A scale factor of 0.0 will collapse the item to a single point. If you provide a negative scale factor, the item will be flipped and mirrored.
The item is scaled around its transform origin point, which by default is (0, 0). You can select a different transformation origin by calling setTransformOriginPoint(). The scale is combined with the item's rotation(), transform() and transformations() to map the item's coordinate system to the parent item.
- See also
- scale(), setTransformOriginPoint()
| void QGraphicsItem::setSelected | ( | bool | selected | ) |
If selected is true and the current QGraphicsItem is selectable this item becomes selected, otherwise it is unselected. If the item is in a group the whole group's selected state is toggled by this method. If the group is selected, all items in the group are also selected, and if the group is not selected, no item in the group is selected.
Only visible, enabled, selectable items can be selected. If selected is true and this item is either invisible or disabled or unselectable, this method does nothing. By default items can not be selected. To enable selection set the ItemIsSelectable flag.
This method is provided to allow individual toggling of the selected state of an item. It is more common to call QGraphicsScene::setSelectionArea(), which will invoke this method for all visible, enabled, and selectable items within a specified area on the scene.
| void QGraphicsItem::setToolTip | ( | const QString & | toolTip | ) |
| void QGraphicsItem::setTransform | ( | const QTransform & | matrix, |
| bool | combine = false |
||
| ) |
Sets the current QGraphicsItem transformation to matrix. If combine is true, then matrix is combined with the current matrix, otherwise matrix replaces the current matrix.
To simplify interaction with items using a transformed view, QGraphicsItem provides mapTo... and mapFrom... methods that can translate between item and scene coordinates. For example, you can call mapToScene() to map an item coordinate to a scene coordinate, or mapFromScene() to map from scene coordinates to item coordinates.
The transformation matrix is combined with the item's rotation(), scale() and transformations() into a combined transformation that maps the item's coordinate system to its parent.
| void QGraphicsItem::setTransformations | ( | const QList< QGraphicsTransform * > & | transformations | ) |
Sets a list of graphics transformations which currently apply to this item. If you only rotate or scale an item, it may be simpler to call setRotation() or setScale(). If you want to set an arbitrary transformation on an item, use setTransform().
QGraphicsTransform is for applying and controlling a chain of individual transformation operations on an item. It is particularly useful in animations where each transform operation needs to be interpolated independently, or differently. The transformations are combined with the item's rotation(), scale() and transform() to map the item's coordinate system to the parent item.
| void QGraphicsItem::setTransformOriginPoint | ( | const QPointF & | origin | ) |
Sets the origin point for the transformation in item coordinates.
- See also
- transformOriginPoint()
This method is equivalent to calling setTransformOriginPoint(QPointF(x, y)).
- See also
- setTransformOriginPoint()
| void QGraphicsItem::setVisible | ( | bool | visible | ) |
If visible is true the item is made visible, otherwise, the item is made invisible. Invisible items are not painted nor do they receive any events. In particular, mouse events pass right through invisible items, and are delivered to any item that may be behind. Invisible items are also unselectable, they can not take input focus, and are not detected by QGraphicsScene's item location methods.
If an item becomes invisible while grabbing the mouse it will automatically lose the mouse grab and the grab is not regained by making the item visible again. In this case the item must receive a new mouse press to regain the mouse grab. Similarly, an invisible item can not have focus, so if the item has focus when it becomes invisible, it will lose focus, and the focus is not regained by simply making the item visible again.
If you hide a parent item, all its children will also be hidden. If you show a parent item, all children will be shown, unless they have been explicitly hidden.
Items are visible by default and it is unnecessary to call setVisible() on a new item.
- See also
- isVisible(), show(), hide()
| void QGraphicsItem::setX | ( | qreal | x | ) |
| void QGraphicsItem::setY | ( | qreal | y | ) |
| void QGraphicsItem::setZValue | ( | qreal | z | ) |
Sets the Z-value of the item to z. The Z value decides the stacking order of sibling (neighboring) items. A sibling item of high Z value will always be drawn on top of another sibling item with a lower Z value.
If you restore the Z value, the item's insertion order will decide its stacking order. The Z-value does not affect the item's size in any way. The default Z-value is 0.
|
virtual |
Returns the shape of this item as a QPainterPath in local coordinates. The shape is used for many things, including collision detection, hit tests, and for the QGraphicsScene::items() methods.
The default implementation calls boundingRect() to return a simple rectangular shape, but subclasses can reimplement this method to return a more accurate shape for non-rectangular items. For example, a round item may choose to return an elliptic shape for better collision detection.
The outline of a shape can vary depending on the width and style of the pen used when drawing. If you want to include this outline in the item's shape, you can create a shape from the stroke using QPainterPathStroker.
This method is called by the default implementations of contains() and collidesWithPath().
Reimplemented in QGraphicsSimpleTextItem::shape(), QGraphicsTextItem::shape(), QGraphicsPixmapItem::shape(), QGraphicsLineItem::shape(), QGraphicsPolygonItem::shape(), QGraphicsEllipseItem::shape(), QGraphicsRectItem::shape(), QGraphicsPathItem::shape()
|
inline |
This method is equivalent to calling setVisible(true).
- See also
- hide(), setVisible()
| void QGraphicsItem::stackBefore | ( | const QGraphicsItem * | graphicsItem | ) |
Stacks this item before graphicsItem, which must be a sibling item. The graphicsItem must have the same Z value as this item, otherwise calling this method will have no effect.
By default all sibling items are stacked by insertion order which means the first item you add is drawn before the next item you add. If two item's Z values are different, then the item with the highest Z value is drawn on top. When the Z values are the same the insertion order will decide the stacking order.
| QGraphicsObject * QGraphicsItem::toGraphicsObject | ( | ) |
Return the graphics item cast to a QGraphicsObject, if the class is actually a graphics object, otherwise returns a nullptr.
| const QGraphicsObject * QGraphicsItem::toGraphicsObject | ( | ) | const |
Return the graphics item cast to a QGraphicsObject, if the class is actually a graphics object, otherwise returns a nullptr.
| QString QGraphicsItem::toolTip | ( | ) | const |
Returns the current QGraphicsItem tool tip or an empty QString if no tool tip has been set.
- See also
- setToolTip(), QToolTip
| QGraphicsItem * QGraphicsItem::topLevelItem | ( | ) | const |
Returns the current QGraphicsItem top level item which is the ancestor whose parent is a nullptr. If the current item has no parent then a pointer to itself is returned.
- See also
- parentItem()
| QGraphicsWidget * QGraphicsItem::topLevelWidget | ( | ) | const |
Returns the current QGraphicsItem top level widget which is the ancestor whose parent is either a nullptr or not a widget. If the item is its own top level widget, this method returns a pointer to the item itself. If the item does not have a top level widget then nullptr is returned.
| QTransform QGraphicsItem::transform | ( | ) | const |
Returns the current QGraphicsItem transformation matrix. The transformation matrix is combined with the item's rotation(), scale() and transformations() into a combined transformations for the item. The default transformation matrix is an identity matrix.
- See also
- setTransform(), sceneTransform()
| QList< QGraphicsTransform * > QGraphicsItem::transformations | ( | ) | const |
Returns a list of graphics transforms which currently apply to this item.
QGraphicsTransform is for applying and controlling a chain of individual transformation operations on an item. It is particularly useful in animations where each transform operation needs to be interpolated independently, or differently. The transformations are combined with the item's rotation(), scale() and transform() to map the item's coordinate system to the parent item.
| QPointF QGraphicsItem::transformOriginPoint | ( | ) | const |
Returns the origin point for the transformation in item coordinates. The default is QPointF(0,0).
- See also
- setTransformOriginPoint()
|
virtual |
Returns the type of the current QGraphicsItem as an integer. All standard graphicsitem classes are associated with a unique value, refer to QGraphicsItem::Type. The type information is used by qgraphicsitem_cast() to distinguish between types. The default implementation returns UserType.
To enable use of qgraphicsitem_cast() with a custom item, reimplement this method and declare a Type enum value equal to your custom item's type. Custom items must return a value larger than or equal to UserType (65536).
- See also
- UserType
Reimplemented in QGraphicsItemGroup::type(), QGraphicsSimpleTextItem::type(), QGraphicsTextItem::type(), QGraphicsPixmapItem::type(), QGraphicsLineItem::type(), QGraphicsPolygonItem::type(), QGraphicsEllipseItem::type(), QGraphicsRectItem::type(), QGraphicsPathItem::type(), QGraphicsSvgItem::type()
| void QGraphicsItem::ungrabKeyboard | ( | ) |
Releases the keyboard grab.
- See also
- grabKeyboard(), ungrabMouse()
| void QGraphicsItem::ungrabMouse | ( | ) |
Releases the mouse grab.
- See also
- grabMouse(), ungrabKeyboard()
| void QGraphicsItem::unsetCursor | ( | ) |
Clears the cursor from this item.
- See also
- hasCursor(), setCursor()
Schedules a redraw of the area covered by rectF in this item. Call this method whenever your item needs to be redrawn, for example if it changes appearance or size. This method does not cause an immediate paint. Instead it schedules a paint request that is processed by QGraphicsView after control reaches the event loop. The item will only be redrawn if it is visible in any associated view.
As a side effect of the item being repainted, other items that overlap the area rect may also be repainted. If the item is invisible (i.e., isVisible() returns false), this method does nothing.
- See also
- paint(), boundingRect()
This method is equivalent to calling update(QRectF(x, y, width, height)).
|
protected |
Updates the current QGraphicsItem micro focus.
|
protectedvirtual |
The event handler for event can be reimplemented to receive wheel events for this item. If you reimplement this method, event will be accepted by default. If you ignore the event it will propagate to any item beneath this item. If no items accept the event, it will be ignored by the scene, and propagate to the view.
The default implementation ignores the event.
- See also
- sceneEvent()
| QGraphicsWidget * QGraphicsItem::window | ( | ) | const |
Returns the item's window or nullptr if this item does not have a window. If the item is a window it will return itself, otherwise it will return the closest ancestor which is a window.
- See also
- QGraphicsWidget::isWindow()
| qreal QGraphicsItem::zValue | ( | ) | const |
Returns the Z-value of the item. The Z-value affects the stacking order of sibling (neighboring) items. The default Z-value is 0.
Friends And Related Function Documentation
|
related |
Member Data Documentation
|
staticconstexpr |
The lowest value returned by the type() method for custom sub classes of QGraphicsItem.


